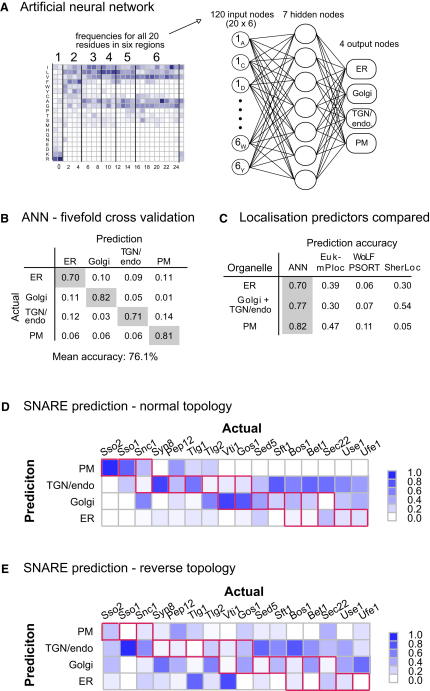
Figure 6.
An Artificial Neural Network Classifier of Subcellular Location Based on TMD Sequence
(A) Overview of the neural network used for classifying proteins. The compositions of six regions along the TMDs from each fungal organelle set were encoded into input vectors to train the network.
(B) Test of the accuracy of the ability of the neural network to predict localization. Performance was assessed using a 5-fold “leave-one-out” cross-validation in which groups of proteins were removed from the training set and then used to test the network trained with the remaining proteins. The predicted location was that with the highest score, with a mean accuracy calculated over all proteins in each set.
(C) A comparison of predictive accuracy of the network (ANN) to that of existing subcellular localization prediction methods when applied to the S. cerevisiae reference proteins.
(D and E) Prediction of SNARE localization using the neural network trained on TMD regions. The SNAREs from S. cerevisiae and 36 other fungi were examined with the network trained on the datasets that do not include the SNAREs, and the frequencies of predictions were normalized and plotted in a matrix against subcellular locations. Red boxes indicate the experimentally determined localizations of the SNAREs. SNARE TMD sequences were reversed prior to analysis in (E).