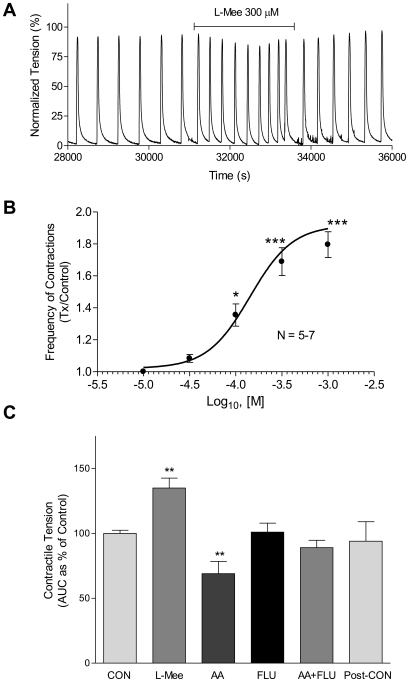
Figure 6. L-methionine ethyl ester increases frequency of contraction in a dose-dependent manner.
L-Mee increased contractile frequency in non-laboring myometrial strips in a concentration-dependent manner (30 µM to 300 mM). Iberiotoxin (100 nM) was present to block Ca2+-activated currents and tissues established spontaneous contractions before drug addition. (A) 30 µM L-Mee applied to the bath caused a slight increase in frequency of contraction, with recovery after washout. (B) 100 µM L-Mee caused a significant increase in frequency of contraction that was pronounced at 300 µM L-Mee with recovery after washout; 1 mM L-Mee caused a marked increase in frequency of contraction with modest, variable reduction in peak amplitude that remained after washout (not shown). (C) In a similar set of tissues, arachidonic acid (AA) significantly depressed contractions, an effect blocked by fluphenazine (FLU; 100 µM), while addition of fluphenazine alone had no significant effect. The effect of L-Mee to increase contractions was not different when added in the presence of 100 µM AA (not shown). Tissues returned to control tension after washout. Data are mean ± SEM, ** = p<0.05, n = 7.