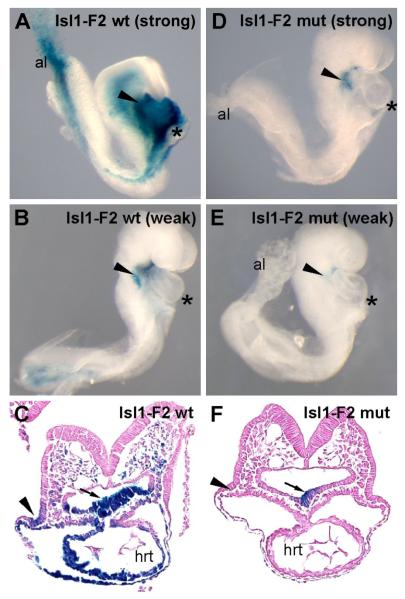
Fig. 5.
The Isl1-F2 SHF enhancer is dependent on Forkhead transcription factor binding sites for enhancer activity in vivo. Transgenic embryos harboring Isl1-F2 wild-type (wt) transgenes (A-C) or Isl1-F2 triple FOX mutant (mut) transgenes (D-F) were collected at E8.5 and X-gal-stained, and the lateral right-sided views of whole-mount embryos (A, B, D, E) and transverse sections (C, F) are shown. Examples of strong (A) and weak (B) transgenic lines harboring the wild type Isl1-F2 transgene exhibited specific expression to the pharyngeal mesoderm and pharyngeal endoderm, as well as in the outflow tract myocardium with variable degrees of expression strength depending on the specific transgenic line. (D, E) By contrast, embryos transgenic for the triple FOX mutant Isl1-F2 construct showed either weak or no expression in SHF derivatives and showed no expression in the outflow tract. (C, F) Transverse sections of transgenic embryos with strong expression of the wild type Isl1-F2-lacZ transgene (C) or strong expression of the triple FOX mutant Isl1-F2-lacZ (mut) transgene (F) show that while the wild type transgene was active in the pharyngeal mesoderm (arrowheads), pharyngeal endoderm (arrows) and SHF mesoderm-derived lineages in the heart (hrt), the mutant transgene was only weakly active in pharyngeal endoderm and showed no activity in SHF-derived mesoderm or any of its mesodermal derivatives. Asterisks denote the heart in panels A, B, D, and E.