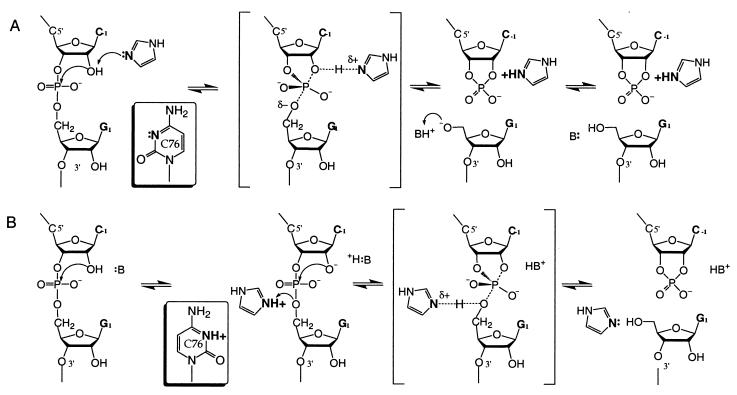
Figure 4.
Two kinetically equivalent mechanisms for general acid-base catalysis by RNA side chains or imidazole buffer. (A) In the C76u and C76Δ mutants, the unsaturated ring nitrogen of imidazole base accepts the proton from the nucleophilic group for general-base catalysis; in the wild type, cytosine serves a similar role. An unidentified functional group stabilizes the leaving group. (B) Imidazolium or protonated cytosine sidechain acts as a general acid by donating a proton to the leaving group. A specific base deprotonates the 2′-OH nucleophilic group at pre-equilibrium.