Figure 1.
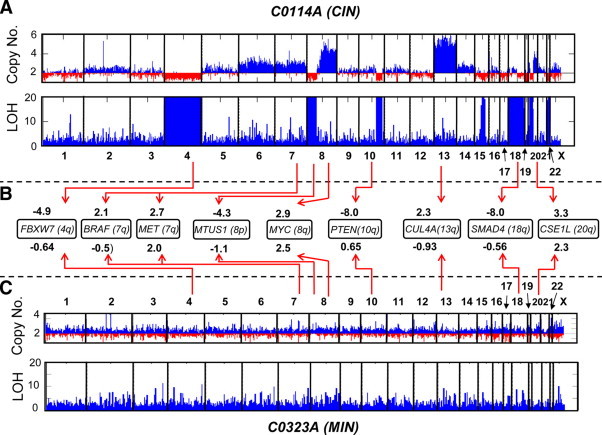
Cytogenetic characterization of CIN (primary tumor sample C0114A; A) and MIN (primary tumor sample C0323A; C) CRC genomes by Affymetrix Xba 240 50K SNP array analysis. As shown here, as well as previously,21 C0114A has acquired copy number losses in chromosomes 4, 22, 8p, and 20p, and gains in chromosomes 7, 8q, 13, and 20q. Also lost were significant portions of 18q and 10q. Unlike C0114A, C0323A did not have noticeable copy number aberrations. B is a comparison of the expression levels of some of the known oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes between the two tumor samples. For example, the expression level (z) of the tumor suppressor gene SMAD4 in C0114A and C0323A (relative to normal colon) are −8.0 and −0.56, respectively. This suggests that the loss of chromosome 18q contributed to C0114A's low mRNA level for SMAD4. Compared with C0323A, C0114A also exhibited lower expression levels for the tumor suppressor genes FBXW7, PTEN, and MTUS1, which are all located in chromosomal regions lost in C0114A. The oncogenes MYC, MET, BRAF, and CUL4A are all located in regions of gain in the C0114A genome. This may explain why C0114A has relatively higher expression levels (at varying degrees) of these genes. ; where It is the normalized, log transformed intensity value (I) of the Affymetrix U133A probe set for the tumor sample, while and σn are the average and SD (respectively) of the I values for 53 normal colon samples. For each gene represented by multiple probe sets (PTEN,CSE1L, MET,MTUS1, CUL4A, SMAD4), the z value indicated in B is actually the average for all probe sets representing the gene. Note: Each genome-wide scan includes a copy number chart (baseline copy number is 2) and LOH chart. High LOH values (for the charts, the LOH value is capped at 20), indicated by tall blue bars represent segments in the chromosome of contiguous homozygous SNPs. Regions of copy loss usually correspond to regions of high LOH.
