Figure 1.
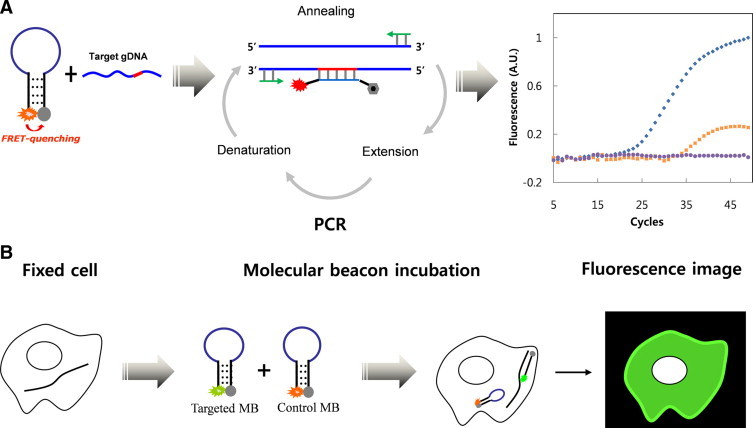
Schematic representation of the detection principle using a molecular beacon. A: Molecular beacon-based real-time PCR. Molecular beacons complementary to a target DNA bind at the annealing temperature, dissociating the stem, and generate a fluorescence signal during real-time PCR. With an increasing number of PCR cycles, fluorescence intensity increases, enabling the detection of the mutation in real-time. B:In situ fluorescence imaging of individual cells carrying a specific mutation. The molecular beacons bind to a target mRNA in the fixed cells, dissociating the stem, and restore a fluorescent signal.
