Figure 1.
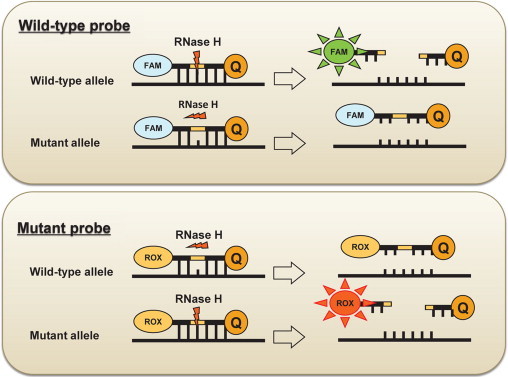
Schematic representation of the Cycleave method. The probe is an RNA-DNA chimera that hybridizes to either the mutated or the wild-type sequence of the amplified gene. Once the probe is hybridized to the amplified products, the RNA part of the probes is cleaved by RNase H, which specifically recognizes complete RNA-DNA hybrids. The cleavage led to two products with the fluorescer and quencher on each side of the probe that emitted fluorescence, when separated. In the case of a mismatch or incomplete hybridization of the RNA part of the probes and amplified products, RNase H does not affect the probe. The mutant probe was labeled with FAM, while the wild-type probe was labeled with ROX. Because the two probes were mixed and reacted simultaneously, the assay was monitored using the signal of the wild-type probe as an internal control.
