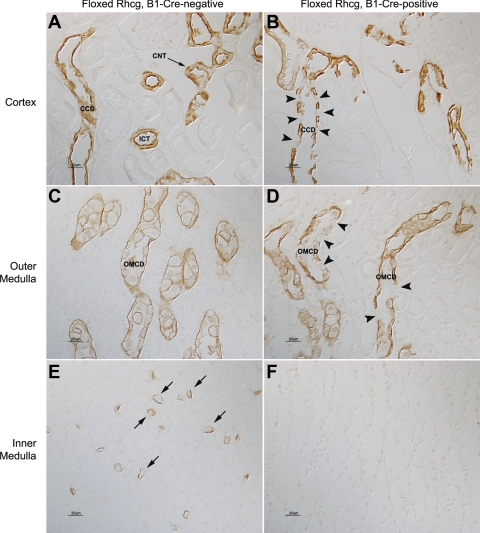
Fig. 1.
Rh glycoprotein C (Rhcg) immunolabel in floxed Rhcg, B1-Cre-negative, and floxed Rhcg, B1-Cre-positive mice. A: Rhcg immunolabel in cortex of floxed Rhcg, B1-Cre-negative mouse kidney. The normal apical and basolateral distribution of Rhcg immunolabel in cortical collecting duct (CCD) and in connecting tubule (CNT) and initial collecting tubule (ICT) is present. B: Rhcg immunolabel in floxed Rhcg, B1-Cre-positive mouse kidney. A large subpopulation of cells (arrowheads) has no detectable Rhcg in the CCD. The number of Rhcg-negative cells is greater than the expected number of B-type intercalated cells, a cell population which does not express detectable Rhcg immunolabel. C: Rhcg immunolabel in the outer medulla and demonstration of normal Rhcg expression in outer medullary collecting duct (OMCD) of B1-Cre-negative mouse kidney. D: outer medulla from floxed Rhcg, B1-Cre-positive mouse kidney. A subpopulation of cells in the OMCD (arrowheads) has no detectable Rhcg. E: Rhcg immunolabel in the inner medulla and demonstration of normal Rhcg expression in inner medullary collecting duct intercalated cells (arrows) in B1-Cre-negative mouse kidney. F: inner medulla from floxed Rhcg, B1-Cre-positive mouse kidney. No Rhcg immunolabel is detectable.