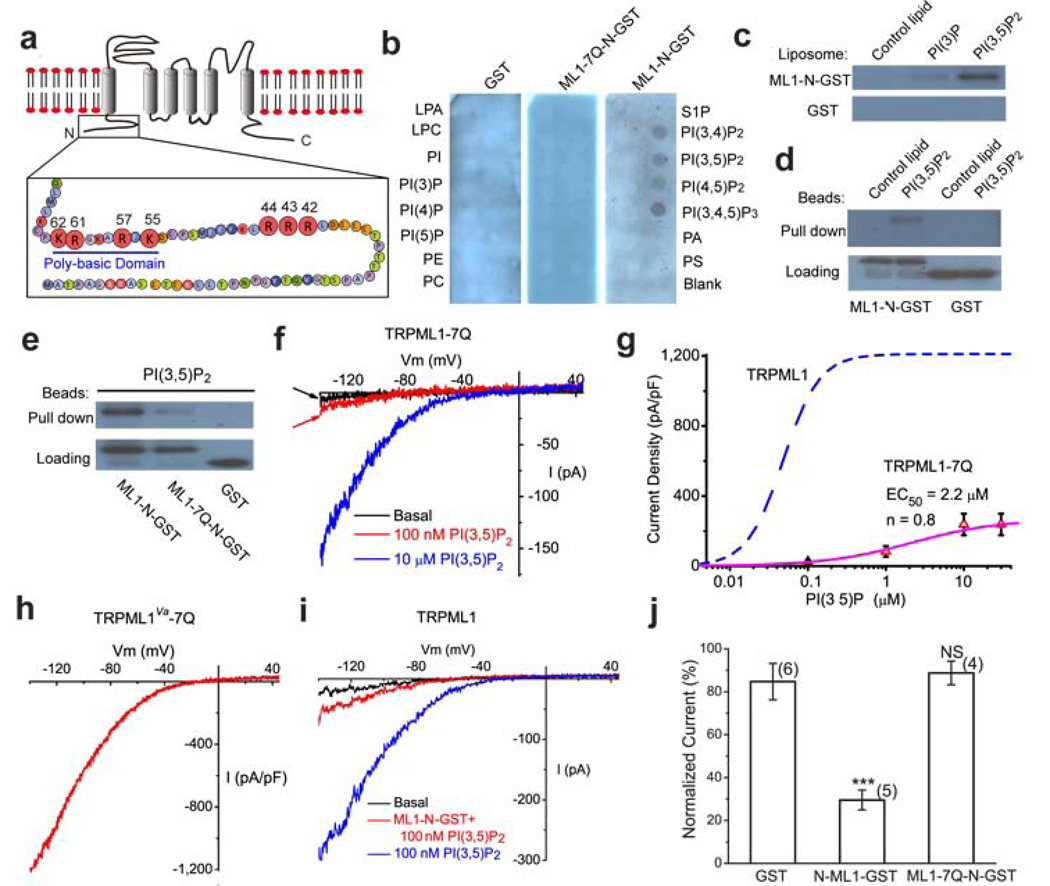
Figure 5. Direct binding of PI(3,5)P2 to the TRPML1 N-terminus requires multiple positively-charged amino acid residues.
a) The cytoplasmic N-terminus of TRPML1 contains a poly-basic region and clusters of positively charged amino acid residues as potential PI(3,5)P2 binding sites. The positively charged amino acid residues (Arg and Lys) that were mutated into neutral amino acids Gln (Q) in this study are shown with enlarged circles and their amino acid residue numbers. b) Protein-lipid overlays. The strip contained 15 different types of lipids: PA, phosphatidic acid; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate. Three purified proteins were used to probe the strip: GST alone (left panel), GST-fused to the N-terminal fragment of TRPML1 (ML1-N-GST; right panel), and Gln-substituted mutant of ML1-N-GST (ML1-7Q-N-GST; middle). Proteins were detected with anti-GST antibodies. c) Liposome pull-down assay. Liposomes were incubated with purified GST-fusion proteins, centrifuged, and associated proteins visualized by Western blot with GST antibodies. d) Binding of GST-ML1-N to agarose beads conjugated to PI(3,5)P2, but not control lipids; GST alone failed to pull down PI(3,5)P2-conjugated beads. e) Compared to GST-ML1-N, GST-ML1-7Q-N exhibited significantly weaker binding to PI(3,5)P2-conjugated agarose beads. f) Whole-endolysosome ITRPML1- 7Q was weakly activated by high concentrations of PI(3,5)P2. g) PI(3,5)P2 dose dependence of ITRPML1- 7Q. Dotted line indicates the dose dependence of ITRPML1 (repotted from Fig. 1d). h) Large basal whole-endolysosome ITRPML1-Va-7Q. Charge-removing Gln substitutions (7Q) were introduced into the gain-of-function Va background. i) GST-ML1-N peptide (5 µg/ml) reduced PI(3,5)P2-dependent activation of whole-endolysosome ITRPML1·. j) Charge-removing Gln-substituted substitutions (7Q) abolished the inhibitory effect of GST-ML1-N peptide.