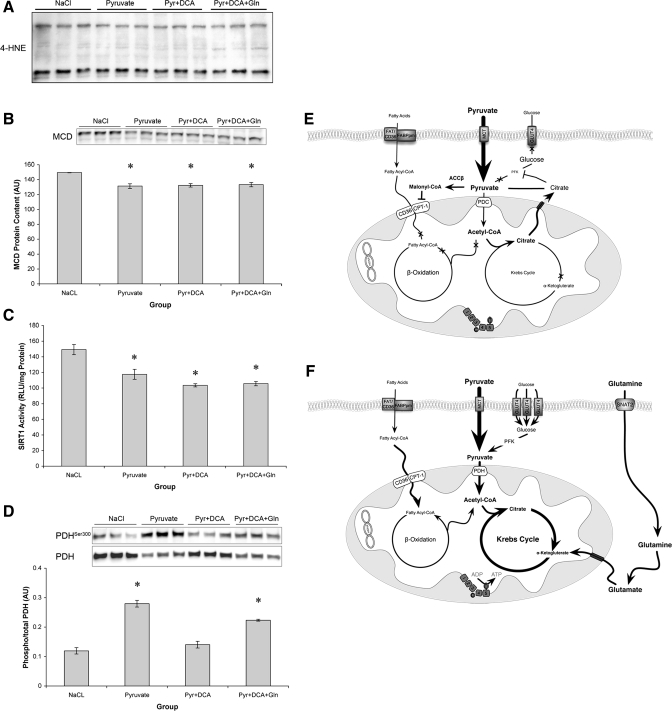
Fig. 7.
Effects of TCA cycle flux on regulators of metabolism. A: absolute levels of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE)-conjugated proteins. B: malonyl-CoA decarboxylase (MCD) protein content relative to teEF2 content. C: SirT1 activity relative to total protein. D: phosphorylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase Ser300 (PDH) relative to total PDH content. *Significantly different from NaCl (P < 0.05). E: proposed model of the effects of pyruvate on C2C12 metabolism. Elevated pyruvate leads to phosphorylation of PDH, suppression of PFK, and reduced GLUT4 and CPT-1 content. Cumulatively, this results in reduced substrate flux through the TCA cycle and suppression of PGC1α. ACCβ, acetyl-CoA carboxylase-β. F: reversal of chronic pyruvate phenotype following the addition of DCA and glutamine. DCA and glutamine addition increases PGC1α expression and GLUT4 and CPT-1 content and alleviates the effect of pyruvate, presumably via increased TCA cycle flux.