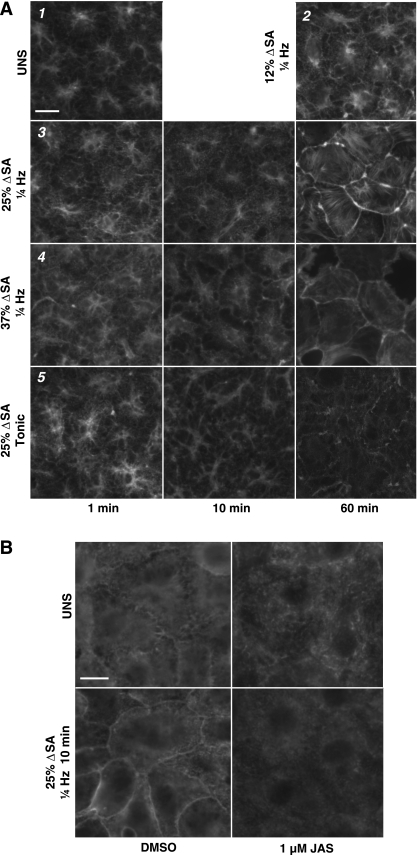
Fig. 1.
A: effect of biaxial stretch duration, magnitude, and frequency on F-actin arrangement in type 1-like rat alveolar epithelial cell (AEC) monolayers before and after 1, 10, and 60 min of stretch (time on x-axis). 1) Monolayers left unstretched (UNS). 2) 12% change of surface area (ΔSA) 0.25-Hz cyclic stretch at 60 min only. 3) 25% ΔSA 0.25-Hz cyclic stretch. 4) 37% ΔSA 0.25-Hz cyclic stretch. 5) 25% ΔSA sustained tonic (0 Hz) stretch. Both 25% and 37% ΔSA 0.25-Hz cyclic stretch produced actin stress fibers on the cell periphery by 10 min, unlike monolayers stretched for 60 min at 12% ΔSA 0.25 Hz cyclic, which were similar to UNS monolayers. Monolayers held sustained tonic 25% ΔSA stretch produced actin stress fibers on the cell periphery at 60 min. Individual micrographs are 56 μm in width. Data at 60 min stretch is comparable at 40 min (not shown). B: effect of biaxial stretch and jasplakinolide (JAS) on actin. Type 1-like rat AEC monolayers with antibody-labeled actin left unstretched (top) or after 10 min of 25% ΔSA 0.25-Hz cyclic stretch (bottom). Vehicle control monolayers (left) stretched at 25% ΔSA produce actin stress fibers on the cell periphery by 10 min, whereas monolayers stretched at the same magnitude and duration treated with 1 μM JAS for 10 min (right) to stabilize actin showed no perijunctional actin ring (PJAR) formation. Bar = 10 μm.