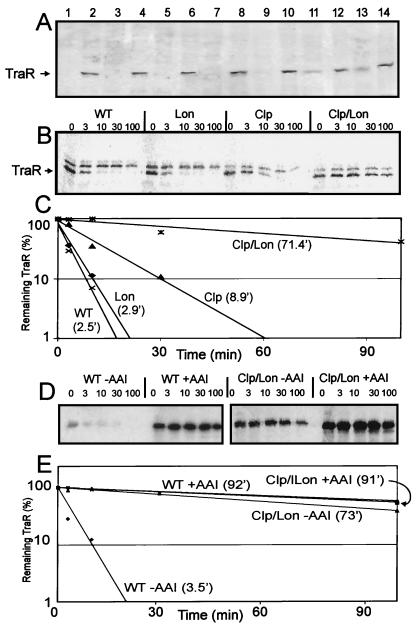
Figure 1.
Apo-TraR accumulation and stability in protease-deficient strains. (A) TraR accumulation assayed with the use of Western immunoblots. Lanes 1 and 2, wild type; lanes 3 and 4, hflB; lanes 5 and 6, hslVU ; lanes 7 and 8, clpP; lanes 9 and 10, lon; lanes 11 and 12, clp, lon; lanes 13 and 14, clp, lon, hslVU. Samples in odd- and even-numbered lanes are from cells cultured in the absence and presence of AAI, respectively. (B) Pulse-labeled TraR in wild-type and protease-deficient E. coli strains. The upper bands are probably due to translation of a particularly stable mRNA from chromosome or a gene containing a T7-like promoter. (C) TraR turnover rates obtained from the data in B. Calculated half-lives are indicated in parentheses. (D) Stabilization of TraR by AAI in wild-type strain and in a clp, lon mutant. (E) TraR turnover rates calculated from data in D.