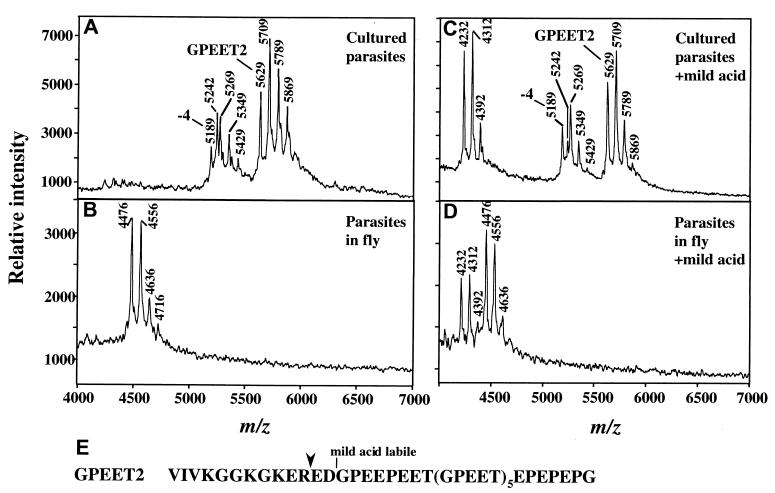
Figure 2.
MS of procyclins from trypanosomes cultured in vitro (A and C) or from tsetse flies three days after infection (B and D). (A) Analysis of aq.HF-treated-procyclins from ≈106 parasites cultured in vitro in the presence of 10 mM glycerol. The ion at m/z 5,629 is full length GPEET2, and it is accompanied by phosphorylated species (m/z 5,709, 5,789, and 5,869). The ion at m/z 5,189 is GPEET2 procyclin truncated by 4 residues, and it is also accompanied by phosphorylated species (m/z 5,269, 5,349, and 5,429). The ion at m/z 5,242 (also present in C) is an unknown polypeptide. Low levels of EP procyclin (EP1–2 and EP3–4) are detected in the 9,000–11,000 m/z range (not shown). (B) Analysis of aq.HF treated-procyclins from ≈7 × 105 parasites extracted from tsetse flies 3 days after infection. The ion at m/z 4,476 is a proteolytic fragment of GPEET2 procyclin (see E for cleavage site), and it is accompanied by ions of phosphorylated species (m/z 4,556, 4636, and 4,716). (C) Mild acid hydrolysis of aq.HF-treated procyclins from cultured trypanosomes, identical to those in A. (D) Mild acid hydrolysis of the aq.HF treated-procyclins from tsetse-derived trypanosomes, identical to those in B. Note in both C and D, the ion of m/z 4,232, representing the C-terminal fragment generated by partial mild acid cleavage at D13 (16). This ion is accompanied by phosphorylated species (m/z 4,312 and 4,392). No fragments of EP procyclins were detected in D. (E) Sequence of GPEET2 procyclin. Downward arrowhead, site of proteolytic cleavage in the fly midgut.