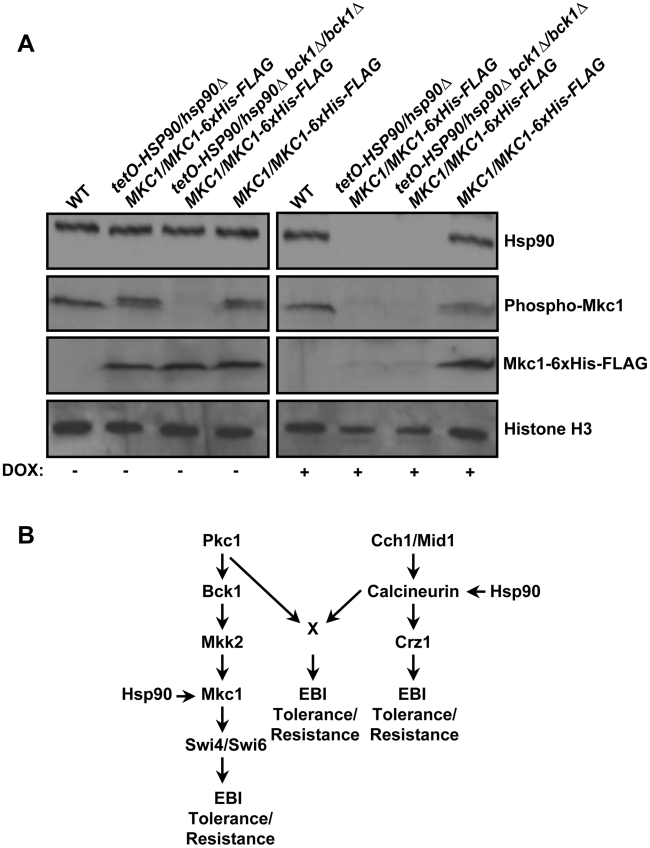
Figure 9. Hsp90 stabilizes the terminal MAPK Mkc1 in C. albicans.
(A) Genetic reduction of Hsp90 levels results in depletion of Mkc1. In strains where the sole allele of HSP90 is under the control of a tetracycline repressible promoter (tetO), transcription of HSP90 can be repressed by tetracycline or the analog doxycycline (DOX). One allele of MKC1 was C-terminally 6xHis-FLAG tagged for monitoring total levels of Mkc1. The MAPKKK Bck1 was deleted to block phosphorylation of Mkc1. Cells were grown with or without DOX (20 µg/ml) before being treated for 3 hours with 50 µg/ml terbinafine (TB) to elicit phosphorylation of Mkc1. Total protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE and blots were hybridized with α-Hsp90, α-His6 to monitor total Mkc1 levels, α-phospho p44/42 MAPK to monitor dually phosphorylated Mkc1 levels, and α-H3 as a loading control. (B) Simplified schematic of how C. albicans Hsp90 governs responses to ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors (EBIs) important for basal tolerance and resistance by regulating both Pkc1-MAPK signaling and calcineurin signaling.