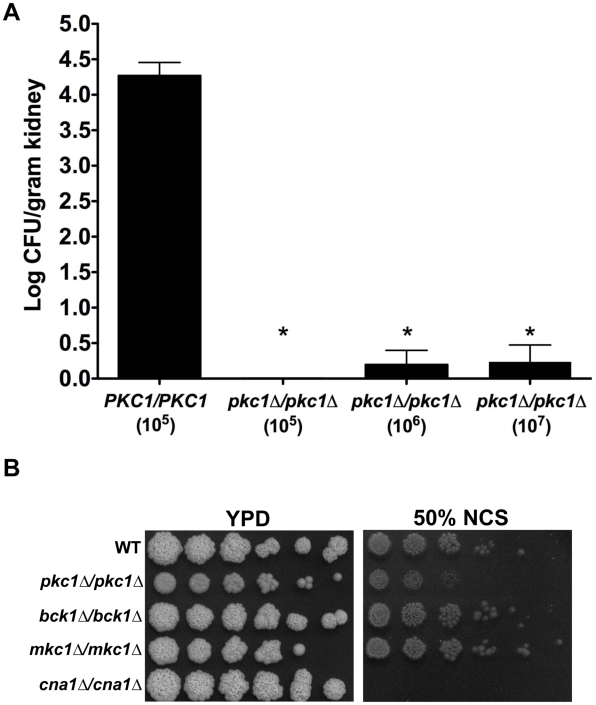
Figure 10. Deletion of C. albicans PKC1 attenuates virulence in a murine model by targets distinct from calcineurin.
(A) CD1 mice were infected with an inoculum of the wild-type strain (SN95) of 1×105 CFU or inoculum of the pkc1Δ/pkc1Δ mutant of 1×105 CFU, 1×106 CFU, or 1×107 CFU. Despite the higher innoculum used, deletion of PKC1 resulted in a dramatic reduction of kidney fungal burden. Asterisks indicate P<0.001 (ANOVA, Bonferroni's Multiple Comparison Test). (B) Deletion of PKC1, but not components of the MAPK cascade, results in a modest increase in sensitivity to serum compared to the hypersensitivity of a mutant lacking the catalytic subunit of calcineurin, Cna1. Cells were spotted in fivefold dilutions (from 1×107 cells/ml for pkc1Δ/pkc1Δ; from 1×106 cells/ml for other strains) onto solid YPD medium with 50% new calf serum (NCS), as indicated. Plates were photographed after 72 hours growth at 35°C.