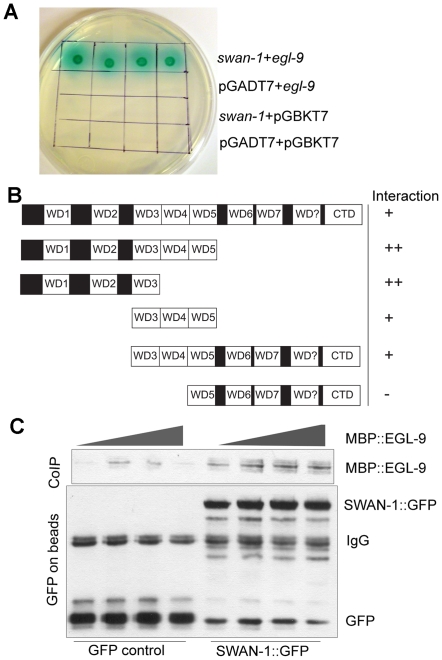
Figure 6. SWAN-1 binds to EGL-9.
A. In yeast two-hybrid assays, SWAN-1 interacted with EGL-9, as assayed by growth on Ade−/His−/Leu−/Trp− media and by α-galactosidase activity with 1×, 10×, 100×, 1000× dilution from left to right. In control experiments, yeast with the bait and prey vectors without inserts (pGADT7 and pGBKT7) did not grow in these conditions. B. SWAN-1 deletions were assayed for interaction with EGL-9 in the yeast two-hybrid system. The relative positions of seven evolutionary conserved WD domains, one degenerate WD domain (labeled WD?) and the C-terminal domain (CTD) are indicated. β-galactosidase activity and growth were scored in at least 3 replicates for each construct, and the strength of the interactions were assessed by comparison to the empty vector pGADT7 negative control (++: p<0.0001; +: 0.000<p<0.05, −: p>0.05). The amino-terminal domain of SWAN-1 containing 3 WD repeats interacted strongly with EGL-9. C. In additional interaction studies, the SWAN-1::GFP protein fusion or GFP was immunoprecipitated from transgenic worms with GFP-specific antibodies coupled to Sepharose beads and then incubated with bacterially-expressed EGL-9 fused to maltose binding protein (MBP::EGL-9). MBP::EGL-9 co-purified with SWAN-1::GFP (lanes 5–8). Negative controls using GFP are shown in lanes 1–4.