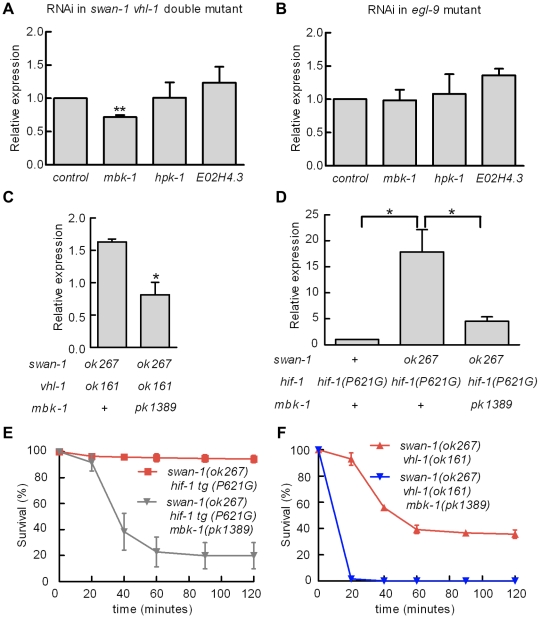
Figure 7. Genetic interactions between swan-1 and mbk-1/DYRK to regulate Pnhr-57::GFP expression and resistance to P. aeruginosa fast killing.
A, B. Bacterially mediated RNAi was used to decrease expression of individual DYRK homologs in C. elegans, and the effects on Pnhr-57::GFP expression was determined by protein blots. The bars show mean values from 3 replicate experiments; error bars represent standard errors. ** p<0.01. A. In swan-1(ok267), vhl-1(ok161) double mutants, mbk-1 RNAi significantly decreased expression of the reporter, but RNAi for the other DYRK homologs did not change Pnhr-57::GFP levels relative to the empty vector control. B. In egl-9(sa307) animals, RNAi for the DYRK homologs tested had no effect on Pnhr-57::GFP. C, D. The mbk-1(pk1389) deletion mutation suppressed Pnhr-57::GFP expression in swan-1(ok267), vhl-1(ok161) double mutant animals (C) and in swan-1(ok267) animals expressing stabilized HIF-1(P621G) protein (D). E, F. The mbk-1(pk1389) mutation suppressed resistance to P. aeruginosa PAO1 in swan-1(ok267) animals. In these experiments, HIF-1 protein was stabilized by either the vhl-1(ok161) loss-of-function mutation (E) or the HIF-1(P621) stabilizing mutation (F). Each experiment was repeated at least three times with 30–50 animals for each strain. The error bars represent standard errors. *: p<0.05; **: p<0.01. These data are presented in tabular format in Text S1.