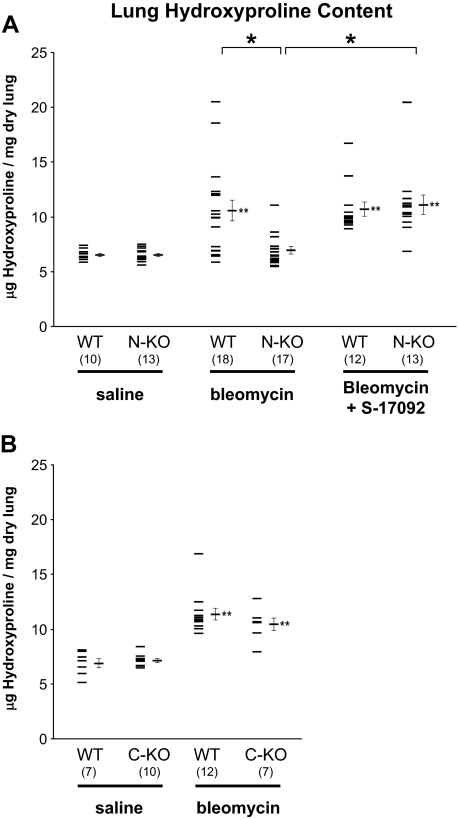
Figure 2.
Lung hydroxyproline content. Inactivation of the N-terminal site of ACE prevents collagen deposition in the lung after bleomycin injection. Lung hydroxyproline content was measured in wild-type (WT) and N-KO mice (A) or C-KO mice (B) two weeks after intratracheal injection of either saline or bleomycin. Because N-KO and C-KO mice are on a mixed 129-C57BL/6 genetic background, appropriate littermate wild-type mice were used for each strain. N-KO and wild-type littermates were also treated with a combination of bleomycin and S-17092, a prolyl-oligopeptidase inhibitor, to reduce the production of AcSDKP. Data points for individual mice are shown, as well as the group means ± SEM. The number of animals per group is indicated in parentheses. *P < 0.01; **P < 0.01 when a group is compared with the saline-treated group of the same genotype (ie, N-KO mice treated with bleomycin/S-17092 versus N-KO mice treated with saline alone). The inactivation of the N-terminal catalytic site of ACE in N-KO mice prevents bleomycin-induced lung collagen deposition. Inhibition of prolyl-oligopeptidase with S-17092 increases bleomycin-induced lung collagen in N-KO mice.