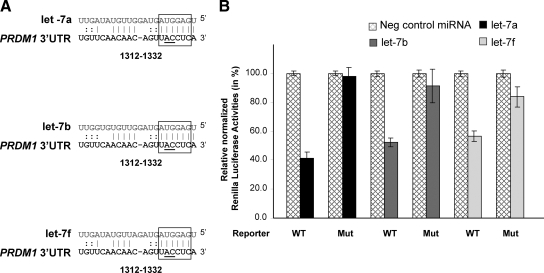
Figure 5.
Let-7 targets PRDM1 3′ UTR. A: Pairing between let-7 family (let-7a, let-7b, and let-7f) and their putative target site in PRDM1 3′ UTR. The highly conserved 6-bp “seed” pairing is highlighted by open boxes. The numbers indicate the locations of the putative binding sites in the PRDM1 3′ UTRs downstream from the PRDM1 stop codon. The nucleotides of the let-7 target site that were mutated (from AC to GT) to disrupt the “seed” pairing are underlined. B: Reporter plasmids harboring PRDM1 3′UTR with wild-type sequence (WT) or point mutations in the let-7 target site (MUT) were cotransfected into 293T cells with let-7a, let-7b, or let-7f (20 nmol/L, Ambion), or with miRNA Negative Control oligonucleotides (20 nmol/L, Ambion). Luciferase activities (in triplicates) were measured 24 hours after transfection. Renilla luciferase activities were normalized against firefly luciferase activities, and mean normalized Renilla luciferase activities (±SE) from three independent experiments were determined and expressed relative to control values. Transfection of let-7 members resulted in about 40% to 60% of inhibition of reporter gene expression, which was relieved by mutations in let-7 binding site.