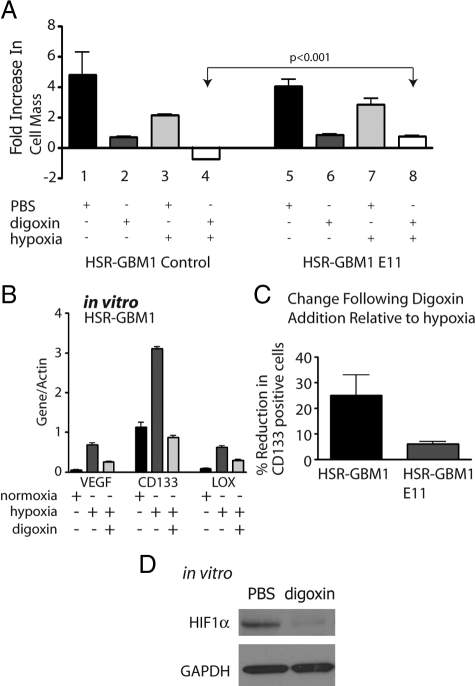
Figure 5.
In vitro digoxin treatments. A: MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide] analysis for HSR-GBM1 vector control and HIF1αP402A/P564A (E11) expressing cells. Growth of HSR-GBM1 was inhibited significantly in the presence of digoxin in normoxia and more so under hypoxia. Fold increase in cell mass was calculated by comparing readings on day five to those of day one. The growth of HSR-GBM1 HIF1αP402A/P564A was also inhibited by digoxin; however, in hypoxia, HIF1α appeared to completely rescue the effect digoxin under hypoxia (compare columns six and eight to columns two and four). (P < 0.001, two-sided t-test). B: Digoxin treatment reduced the expression level of the HIF1α direct targets VEGF and LOX, as well as CD133. Cells were treated with hypoxia or normoxia with PBS or digoxin (100 nmol/L) for 48 hours. C: Flow cytometric analysis of HSR-GBM1 cells, either control or E11 (Expressing oxygen stable form of HIF1α), showed that digoxin treatment reduced CD133 fraction by 25% in HSR-GBM1 control cells, an effect that was partially rescued (to 6%) by constitutive expression of the oxygen stable form of HIF1α. (The average of three independent experiments is shown. D: Western blot analysis for HIF1α in cultured HSR-GBM1 cells treated with digoxin for 24 hours. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase used as even loading control.