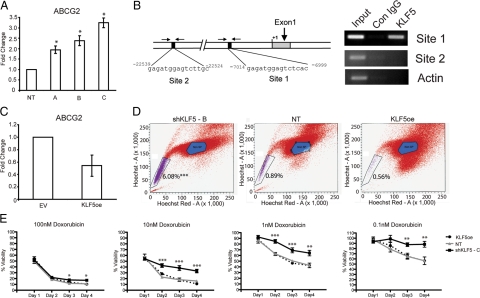
Figure 4.
KLF5 represses ABCG2 expression and controls doxorubicin sensitivity. A: Real-time quantitative gene expression analysis (TaqMan) of ABCG2 in A549 cells transduced with lentiviruses expressing KLF5-specific shRNAs (A, B, and C) or nontargeting shRNA control (NT). B: Schematic representation of the ABCG2 gene with putative KLF5 binding sites 1 and 2 (black boxes). Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis on lysates from A549 cells overexpressing KLF5. KLF5-specific antiserum was used for immunoprecipitation of KLF5-DNA complexes, and the indicated primers flanking sites 1 and 2 (arrows) were used for identification of DNA sequences. Immunoprecipitation using IgG and amplification of β-Actin gene (actin) serve as negative controls. C: Real-time quantitative gene expression analysis (TaqMan) of ABCG2 in A549 cells transduced with retroviral vectors overexpressing KLF5 (KLF5oe) or an empty vector control (vector). D: Side population (SP) shown is purple flow cytometric analysis after Hoechst 33342 dye staining of A549 cells transduced with lentivirus expressing KLF5-specific shRNA “B” (shKLF5-B), nontargeting shRNA control (NT), or a retrovirus overexpressing KLF5 (KLF5oe). The percentages of SP cells per group are indicated. E: WST cell growth analysis of A549 cells transduced with lentivirus expressing KLF5-specific shRNA “C” (shKLF5-C), nontargeting shRNA control (NT), or a retrovirus overexpressing KLF5 (KLF5oe) treated with the indicated doses of doxorubicin. % Viability was calculated as (absorbance of treated cells)/(absorbance of untreated cells) × 100% ± SEM *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, and ***P < 0.0005 by one-way analysis of variance.