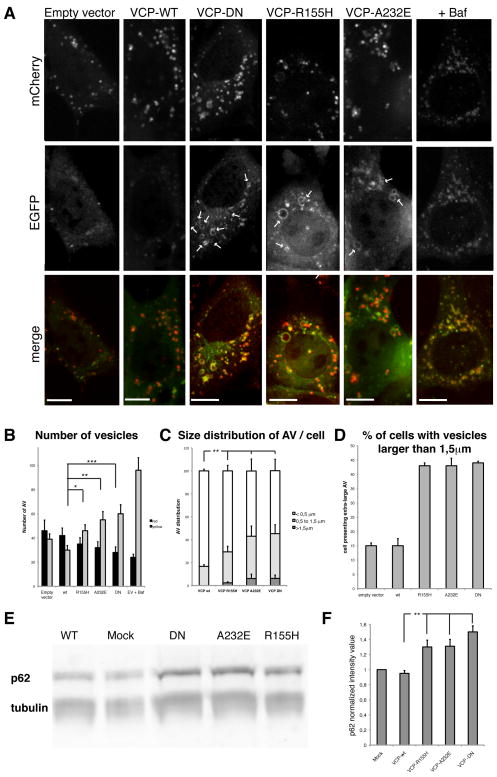
Figure 3. Defective autophagosome maturation in cells expressing disease-associated VCP mutants.
(A) mCherry-EGFP-LC3b stable MEFs transfected with the empty vector or expressing VCP-wt, VCP-DN, VCP-R155H or VCP-A232E. Arrows indicate large LC3-positive vesicles. Scale bars equal 10 μm. (B) Quantification of autophagosomes (yellow) and autophagolysosomes (red) per cell under basal conditions. Cells were transfected with the empty vector, or with VCP-wt, VCP-DN, VCP-R155H or VCP-A232E. Empty vector transfected cells were also treated with bafilomycin (ev +Baf). * indicates p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001. Error bars indicate standard errors. (C) Size distribution of autophagic vesicles (AV) in cells transfected with wt or mutant forms of VCP. Size is estimated in μm. ** indicates p<0.01. (D) Quantification of the percent of cells containing “extra-large” vesicles (i.e. over 1.5 μm diameter) in cells transfected with empty vector, wt-VCP or mutant forms of VCP. Experiment was performed twice in triplicate. (E) Mutant forms of VCP lead to accumulation of p62 in HEK293T cells. Western blot against p62/rabbit and tubulin/mouse using a Li-Cor Odyssey system. (F) Quantification of p62 Western-Blot. p62 quantification was normalized to tubulin quantity. Error bars indicates standard deviation of three independent replicates. ** indicates p<0.01.