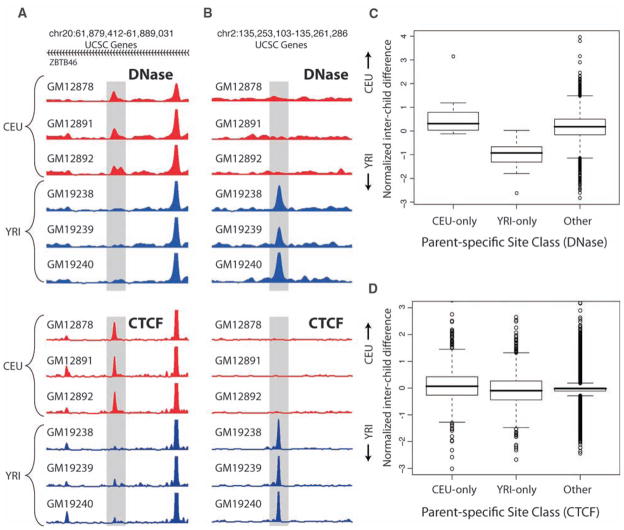
Fig. 2.
Individual-specific chromatin transmission. (A) Example of CEU-only individual-specific DNase I HS and CTCF sites (shaded areas). (B) Example of YRI-only individual-specific sites. (C and D) Genome-wide individual-specific DNase I HS sites (C) and CTCF sites (D) were categorized as CEU-only, YRI-only, or other combinations. The standard box plots of the relative normalized interchild differences for these categories show that the child signal was significantly closer to the parental sites from its own population (P < 10−15 for DNase I HS, P < 10−8 for CTCF; Wilcoxon rank-sum test). Numbers at top of (A) and (B) are chromosome numbers followed by start-stop coordinates from the UCSC Genome Browser. In (A) the indicated sites occur in the ZBTB46 gene, whose direction of transcription is right to left (as indicated by arrowheads).