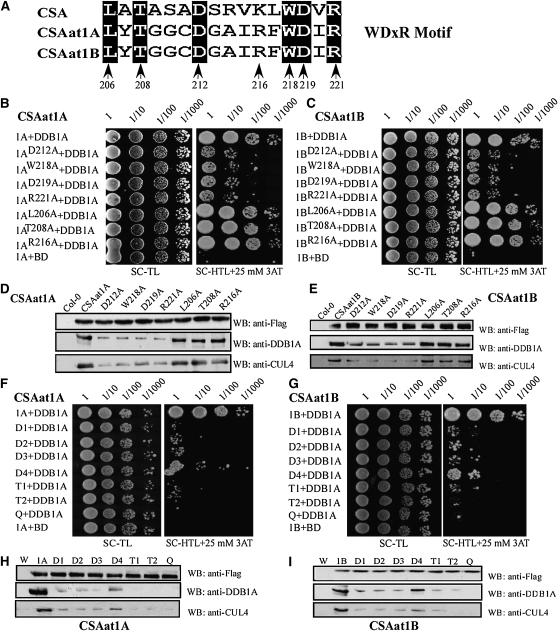
Figure 6.
The WDxR Motif Is Essential for CSAat1A and B Interaction with DDB1A.
(A) Positions of single mutations generated in the WDxR motif. The numbers indicate the amino acid residue in CSAat1A and B. All indicated sites were mutated to Ala (A).
(B) and (C) Effect of single amino acid mutations in the WDxR motif on the interaction between CSAat1A or B and DDB1A in yeast. CSA1at1A or B, CSAat1AD212A or BD212A, CSAat1AW218A or BW218A, CSAat1AD219A or BD219A, CSAat1AR221A or BR221A, CSAat1AL206A or BL206A, CSAat1AT208A, or BT208A and CSAat1AR216A or BR216A in pGADT7 were cotransformed with pGBKT7-DDB1A into yeast. Growth of the transformed yeast was assayed on media minus Trp and Leu (left panels) or minus Trp, Leu, and His with 25 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (right panels). Columns in each panel represent serial decimal dilutions. BD, binding domain.
(D) and (E) Effect of single amino acid mutations in the WDxR motif on the interaction between CSAat1A or B and DDB1A-CUL4 in planta. The CSAat1A- or B-Flag proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag agarose. The pull-down products were analyzed via immunoblots with anti-Flag, anti-DDB1A, or anti-CUL4 antibodies. WB, immunoblot.
(F) and (G) Effect of multiple amino acid mutations in the WDxR motif on the interaction between CSAat1A or B and DDB1A in yeast. CSA1at1A or CSA1at1B (B); D1, CSAat1AD212AW218A or BD212AW218A; D2, CSAat1AD212AD219A or BD212AD219A; D3, CSAat1AD212AR221A or BD212AR221A; D4, CSAat1AL206AD212A or BL206AD212A; T1, CSAat1AD212AW218AD219A or BD212AW218AD219A; T2, CSAat1AW218AD219AR221A or BW218AD219AR221A; and Q, CSAat1A D212AW218AD219AR221A or B D212AW218AD219AR221A in pGADT7 were cotransformed with pGBKT7-DDB1A into yeast. Growth of the transformed yeast was assayed on media minus Trp and Leu (left panels) or minus Trp, Leu, and His with 25 mM 3-amino-1, 2,4-triazole (right panels). Columns in each panel represent serial decimal dilutions. BD, vector pGBKT7.
(H) and (I) Effect of multiple amino acid mutations in the WDxR motif on the interaction between CSAat1A or B and DDB1A-CUL4 in planta. The CSAat1A- or B-Flag proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag agarose. The pull-down products were analyzed via immunoblot analysis with anti-Flag, anti-DDB1A, or anti-CUL4 antibodies. W, wild type; 1A and 1B, 35Spro-CSAat1A- or B-Flag, respectively; D1, 35S-pro-CSAat1AD212AW218A- or BD212AW218A-Flag; D2, 35Spro-CSAat1AD212AD219A- or BD212AD219A-Flag; D3, 35Spro-CSAat1AD212AR221A- or BD212AR221A-Flag; D4, 35Spro-CSAat1AD212AL206A- or BD212AL206A-Flag; T1, 35Spro-CSAat1AD212AW218AD219A- or BD212AW218AD219A-Flag; T2, 35Spro-CSAat1AW218AD219AR221A- or BW218AD219AR221A-Flag; Q, 35Spro-CSAat1AD212AW218AD219AR221A- or BD212AW218AD219AR221A-Flag. WB, immunoblot.