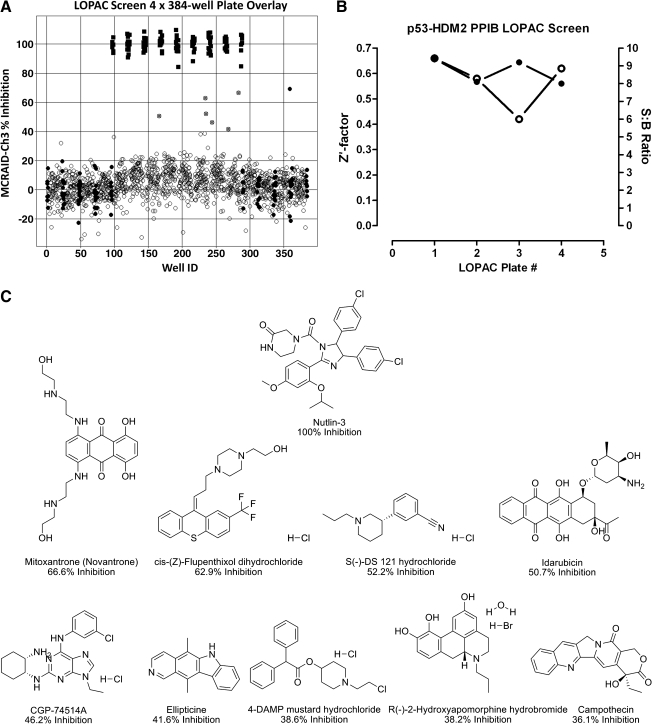
Fig. 6.
p53-hDM2 protein–protein interaction biosensor (PPIB) Library of Pharmacologically Active Compounds (LOPAC) high-content screen. U-2 OS cells were coinfected with the p53-hDM2 PPIB adenoviruses, seeded at 2,500 cells per well in 384-well Greiner collagen-coated assay plates, and cultured overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity as described earlier. Diluted compounds and plate controls were transferred from the 4 × 384-well LOPAC daughter plates or control blocks to the p53-hDM2 PPIB assay plates to provide a final screening concentration of 50 μM and then incubated for 90 min prior to fixation with 3.7% formaldehyde containing 2 μg/mL Hoechst 33342. Images were acquired on the ArrayScan VTI platform and analyzed with the molecular translocation image analysis algorithm as described for Figure 2. The mean circle ring average intensity difference in channel 3 (MCRAID-Ch3) data was used as the primary indicator of the interactions between p53 and hDM2. (A) Four-plate overlay of percent inhibition for the LOPAC Screen. An ActivityBase primary HTS template was created that automatically calculated the percent inhibition. The mean MCRAID-Ch3 value of the dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) minimum plate control wells (●, n = 32 per plate) and the mean MCRAID-Ch3 value of the 10 μM Nutlin-3 maximum plate control wells (▪, n = 24) were used to normalize the MCRAID-Ch3 compound data (○) and to represent 0% and 100% disruption/inhibition of the p53-hDM2 interactions, respectively. Potential active compounds (gray circle, ●) with greater than 40% inhibition are indicated. (B) High-content screening (HCS) performance. An ActivityBase primary HTS template was created, which automatically calculated the plate control signal-to-background (S:B) ratios and Z′-factors using the MCRAID-Ch3 values of the DMSO minimum plate control wells (n = 32 per plate) and the 10 μM Nutlin-3 maximum plate control wells (n = 24). Z′-factors (∘) and S:B ratios (●) for the four 384-well plates of the LOPAC screen. (C) Chemical structures, names, and percent inhibition of the LOPAC HCS actives. The chemical structures, names, and percent inhibition for 9 compounds that exhibited ≥35% inhibition and for Nutlin-3 are presented.