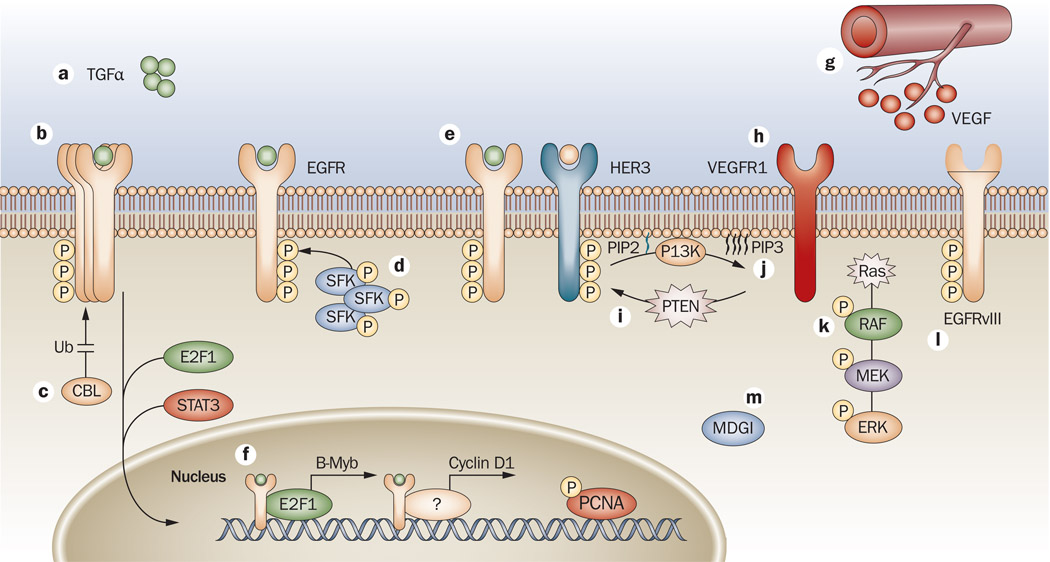
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR antibodies. a | One mechanism of resistance to cetuximab is overexpression of the EGFR ligand TGFα.160 b | Overexpression of EGFR has also been implicated in the development of acquired resistance.117 c | Ubiquitylation is important for mechanisms of escape to cetuximab therapy.117,122 d | Modulation of EGFR by SFKs, and increased activity of SFKs in cetuximab-resistant lines have been reported.122,123 e | The binding and activation of EGFR or HER2 to HER3 has been reported, which allows prolonged signals to the PI3K/AKT pathway.117,123 f | Translocation of EGFR to the nucleus has a role in resistance to cetuximab.125 g | Increased VEGF production leads to altered angiogenesis and enhanced escape from cetuximab therapy.115,116 h | VEGFR1 also contributes to resistance to cetuximab.120 i–j | Mutations in both PTEN and Ras have been implicated in impaired response to cetuximab therapy.96 k | Mutations in KRAS keep it in a constant GTP-bound, active state, allowing it to send signals downstream independently from RTK activation. l | EGFRvIII a truncated form of EGFR that is constitutively phosphorylated in a ligand-independent manner.121,161 m | MDGI alters trafficking of EGFR, leading to resistance to cetuximab therapy.126 Abbreviations: B-Myb, Myb-related protein B; CBL, E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL; E2F1, transcription factor E2F1; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK, mitogen-activated protein kinase 3; MDGI, mammary derived growth inhibitor; P, phosphorylation; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; SFK, Src family kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TGFα, transforming growth factor alpha; Ub, ubiquitylation; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR1, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1.