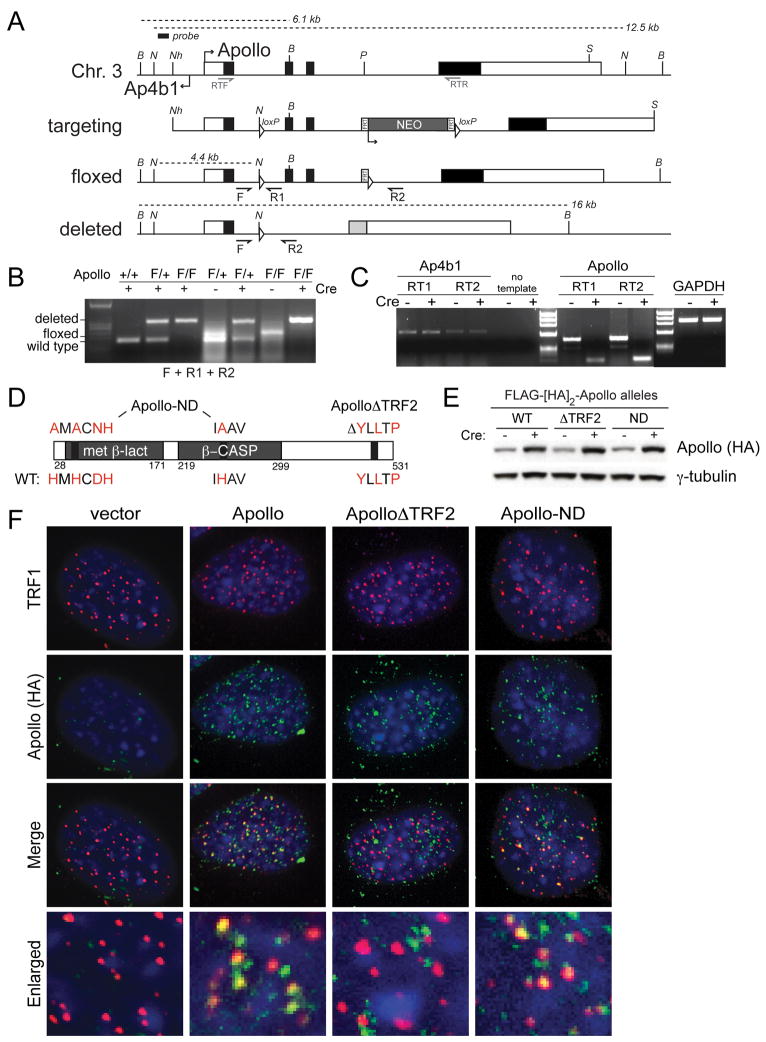
Figure 1. Deletion of mouse Apollo and complementation with mutant alleles.
(A) Targeting of the mouse Apollo locus. The structure of the genomic locus, the targeting construct, the floxed allele and the deleted allele are shown. loxP sites are represented as triangles; FRT sites surrounding the neo gene are shown as rectangles. Approximate positions of the PCR primers for genomic analysis (F and R1 and R2) and RT-PCR mRNA analysis (RTF and RTR) are shown. Restriction endonucleases and the probe used for analysis of genomic DNA: B, BamHI, N, NsiI, Nh, NheI, P, PacI, S, ScaI. (B) Genotyping PCR for Apollo using DNA from MEFs. (C) RT-PCR with two independent sets of primers for both Apollo and Ap4b1 using RNA purified from cells treated with or without Cre. GAPDH was used as a control. (D) Schematic of the mouse Apollo protein indicating regions that are altered in Apollo rescue alleles. Amino acids in red indicate important residues for nuclease activity and TRF2 interaction. (E) Immunoblotting analysis of ApolloF/F MEFs expressing the indicated Apollo alleles in the absence of Cre and at 120h after Cre. Apollo is detected with the HA.11 antibody. (F) Immunofluorescence showing the localization of the indicated Apollo alleles (detected with HA.11 Ab) in ApolloF/F MEFs at 72h after Cre infection. Telomeric loci are detected with Ab 644 to the shelterin component TRF1. DNA is stained with DAPI. See also Figure S1.