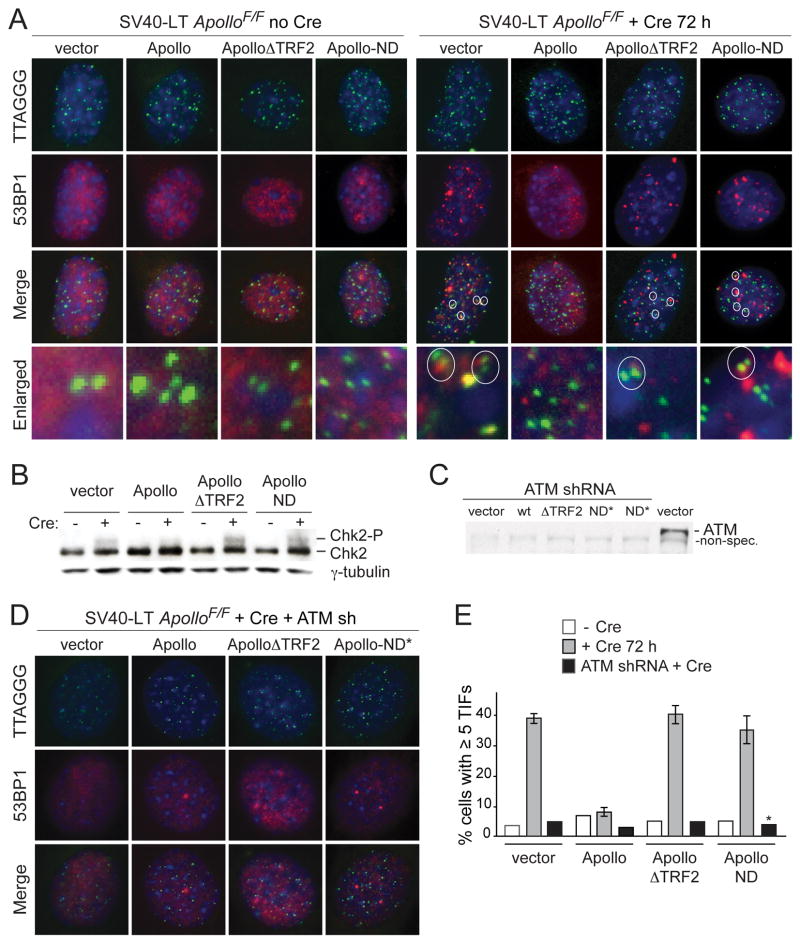
Figure 2. Apollo is required to repress telomeric ATM signaling in S phase.
(A) TIF assay on ApolloF/F MEFs expressing the indicated Apollo alleles to detect telomeric DNA damage signaling before (left) and after (right) deletion of the endogenous Apollo with Cre. Telomeres are detected using a FISH probe (green). DNA damage sites are marked with 53BP1 (red). DNA is counterstained with DAPI (blue). Circled TIFs in the enlarged images highlight the prevalence of TIF occurrence at two closely positioned telomeres or in cells with paired telomeres, indicative of DNA damage signaling during or after telomere replication. (B) Immunoblotting for the phosphorylation state of Chk2 at 6 days after Cre treatment. (C) Immunoblot showing depletion of ATM (Mat3-Sigma) 6 days after shRNA treatment and 3 days after the start of puromycin selection in ApolloF/F MEFs expressing the indicated Apollo alleles. Apollo-ND* is identical to Apollo-ND, except without the mutation of H230. (D) Effect of ATM kinase knockdown on the TIF response in Apollo deficient cells. TIF analysis as in (A) but with cells expressing an shRNA to the ATM kinase. (E) Quantification of TIF responses as assayed in (A) and (D). TIFs were scored on the basis of co-localization of 53BP1 foci with 5 or more telomeres per cell. Values for alleles +Cre indicate the mean of 3 independent experiments (> 100 nuclei per experiment), and SDs. * indicates the use of the Apollo-ND* allele in the ATM shRNA experiment. See also Figure S2.