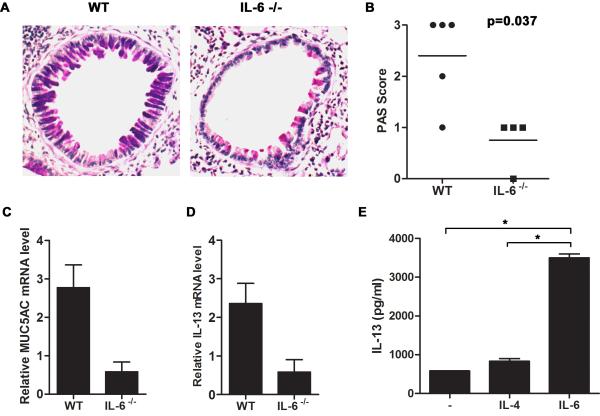
Figure 5.
IL-6 mediates mucus production by lung epithelium through the induction of IL-13 in CD4+ T cells in allergic airway inflammation. (A-D) Wild type (n=5) and IL-6−/− (n=4) mice were exposed to A.f. extracts as described in Fig. 2. (A) Mucus production in the lung was visualized by PAS staining of paraffin embedded lung sections. Photomicrographs from A.f.-challenged wild type (left) and IL-6−/− mice (right) are original magnification, ×200. (B) Histological score indicating intensity of PAS staining for each group (p<0.05). (C) Muc5AC (p<0.05) and (D) IL-13 (p<0.05) expression in the lung were determined by real time RT-PCR and normalized to 18S RNA. (E) Naïve CD4+ T cells from wild type mice were activated in vitro with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 mAbs in the presence or absence of IL-6 (100 ng/ml) or IL-4 (1×103 U/ml). IL-13 was measured in the culture supernatant after 48 h by ELISA in triplicate (*, p<0.05 CD4+ T cells treated with IL-6 compared with cells activated in the presence of medium alone or IL-4).