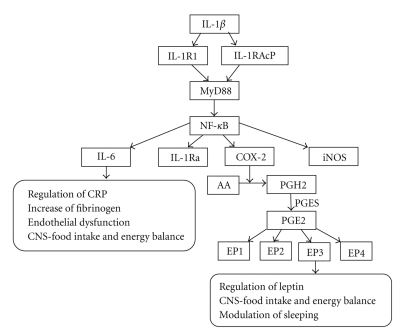
Figure 3.
Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) induction of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) signaling. IL-1β binds to the IL-1R1/IL-1R1AcP heterodimer, which then initiates the signaling cascade that causes the translocation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) into the nucleus, where it induces the transcription of pro- and anti-inflammatory genes including inducible nitric oxide synthetase (iNOS), IL-6, IL-1Ra and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). COX-2 catalyses the conversion of arachidonic acid (AA) to prostaglandin H2 (PGH2). PGH2 is converted into PGE2 by terminal PGE synthase (PGES). PGE2 signals occur via four different G-protein coupled receptors, EP1R-EP4R, each of which has multiple splice variants with different signaling properties.