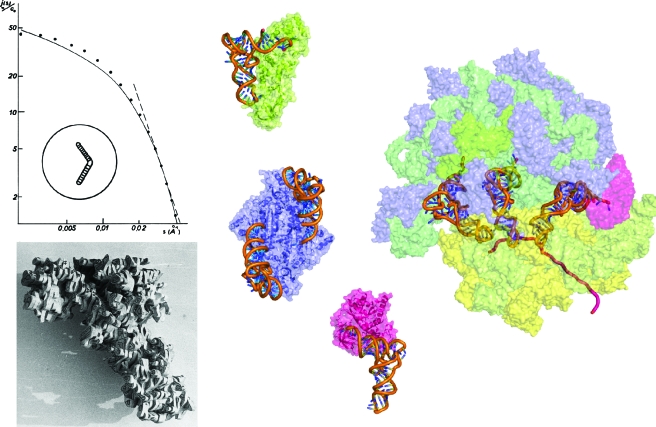
Figure 3. From the single macromolecule to its integration in supramolecular biological systems: the example of transfer RNAs.
(Left) SAXS curve from which a boomerang-shaped model of tRNA was deduced (Witz, 1964; Witz, 2003) and a balsawood model built after the X-ray analysis of yeast tRNAAsp at 3 Å resolution (Moras et al., 1980). (Middle) first X-ray structures of tRNAs in complex with proteins from the translation machinery: E. coli tRNAGln in interaction with monomeric class Ib GlnRS (in green) (Rould et al., 1989), S. cerevisiae tRNAAsp in interaction with its cognate dimeric class IIb AspRS (in blue) (Ruff et al., 1991), and phenylalanyl-tRNAPhe in interaction with bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu (in pink) (Nissen et al., 1995). (Right) view of the E. coli ribosome in translation with the three tRNA molecules bound to A, P, and E sites obtained by fitting an atomic model (derived from X-ray structures) in a 6.7 Å resolution cryo-EM map (Villa et al., 2009). Ribosomal proteins from 30 S and 50 S subunits are shown in yellow and blue, respectively, and 23 S, 5 S, and 16 S RNAs in dark, medium, and light green, respectively. The mRNA is symbolized by a violet ribbon and the tRNA in the A site is bound to EF-Tu (pink). Models in the middle and on the right are shown at the same scale.