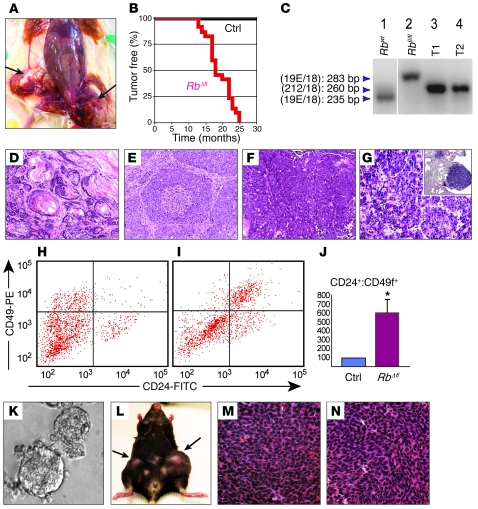
Figure 4. MMTV-Cre:Rbfl/fl and MMTV-Cre:Rbfl/fl:p107–/– mice develop transplantable mammary tumors.
(A) Dissected MMTV-Cre:Rbfl/fl:p107–/– female with 2 large tumors in mammary gland nos. 4 and 5 (arrows). (B) Tumor-free curve for a cohort of 22 RbΔfl mice (2 MMTV-Cre:Rbfl/fl:p107+/+, 12 MMTV-Cre:Rbfl/fl:p107–/– and 8 MMTV-Cre:Rbfl/fl:p107+/–) and 20 control (without MMTV-Cre) littermates. (C) Complex PCR analysis with the 3 primers. Lane 1, Rb+/+ mouse tail; lane 2, Rbfl/fl mouse tail; lane 3, MMTV-CreNLST:Rbfl/fl:p107–/– mammary tumor; lane 4, MMTV-CreD:Rbfl/+:p107+/– heterozygote mammary tumor, demonstrating LOH at the Rb locus. Lanes were run on the same gel but were noncontiguous (white line). (D–G) H&E staining of representative RbΔfl tumors and pulmonary metastasis. (D) Tumor 2, adenosquamous carcinoma. (E) Tumor 4, solid adenocarcinoma with comedo patterns. (F) Tumor 9, adenocarcinoma with cystic changes. (G) Pulmonary metastasis in MMTV-Cre:Rbfl/fl:p107–/– mutant shown in F. Note glandular tumors with histology similar to the original tumor. Inset: low-magnification image of the pulmonary metastasis (right; normal lung tissue on left). (H and I) CD24-CD49f flow cytometry profiles of Lin– control mammary gland (H) and RbΔfl tumor (I). (J) Mean Lin–CD24+CD49f+ cells in RbΔfl mammary tumors (n = 4) relative to Lin– mammary epithelial cells from control littermates (n = 6). P < 0.01. (K–N) RbΔfl mammary tumor cells were transplantable. (K) Secondary RbΔfl tumorspheres cultured for 2 weeks. (L) A Rag1–/– female mouse with secondary RbΔfl mammary tumors arising after transplantation of 10,000 and 1,000 tumorsphere cells into the right and left, respectively, of mammary gland no. 4. (M) Primary, poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. (N) Secondary tumor after transplantation of tumorsphere cells derived from the tumor in M. Original magnification, ×200 (D–F); ×400 (G, M, and N); ×100 (G, inset); ×20 (K).