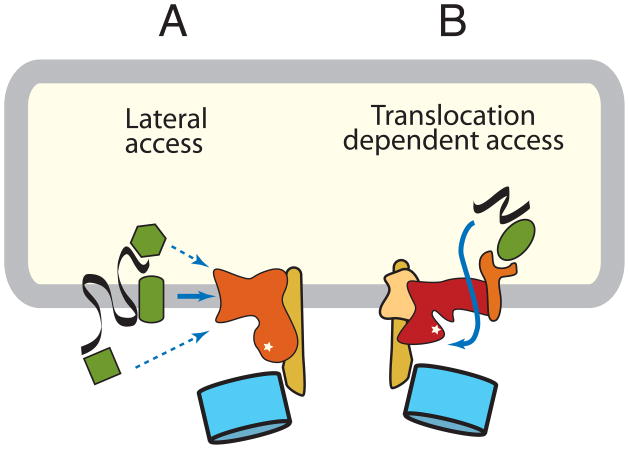
Figure 3. Pathways of substrate ubiquitination.
Membrane ubiquitin ligase complexes mediate substrate access to the catalytic site by two distinct mechanisms. (A) Membrane protein substrates might access the catalytic site by lateral delivery. Recognition and targeting might be mediated by an adaptor in the membrane, cytosol, or lumen. Alternatively, the ubiquitin ligase complex itself could recognize some substrates. (B) Lumenal substrates and some membrane proteins access the catalytic site by a translocation-dependent mechanism. The mechanism or components mediating the key translocation step to provide initial substrate access is unknown, but might involve the ubiquitin ligase itself or an associated membrane protein. In yeast, a complex centered around the Doa10 ubiquitin ligase is probably an example of the first pathway, while a complex containing the Hrd1 ubiquitin ligase is an example of the second pathway. In mammals, many additional similar complexes built around other ubiquitin ligases exist, although their compositions remain to be clearly defined.