Figure 4. FH2 domain structure and elongation model of formin-mediated actin polymerization.
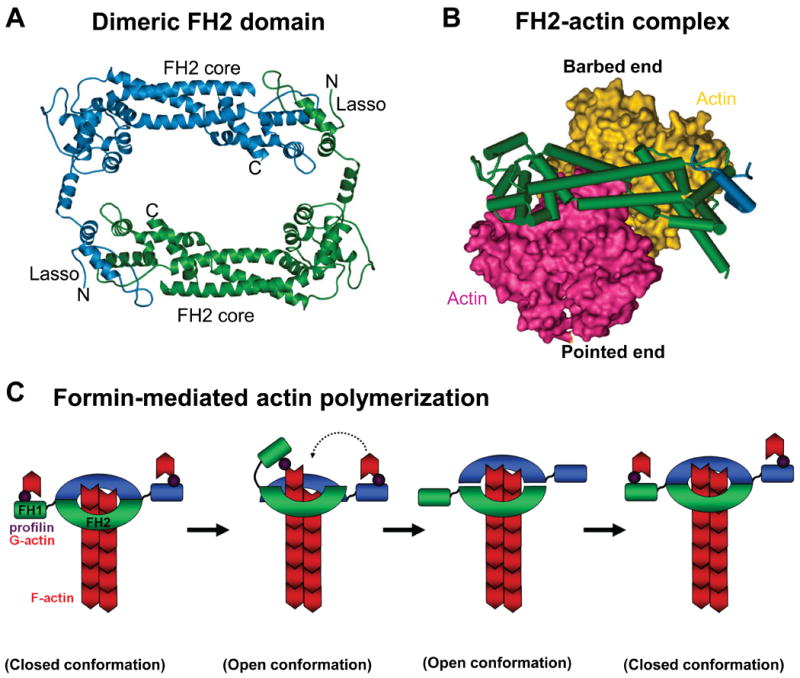
A) A ribbon diagram of the dimeric FH2 domain from S.cerevisiae Bni1 is shown (Ref.89). A “lasso” extends from the knob of one monomer and wraps around the “post” of the other monomer to stabilize this dimeric configuration. FH, formin homology.
B) The Bni1p FH2 domain wrapped around a space-filling model of an actin dimer is shown.
C) An FH2 dimer associates with the barbed end of an actin filament, while the FH1 domains recruit profilin-actin (1). The FH1 domain delivers profilin-actin to the barbed end, and this is either preceded by (Ref.92) or follows (Ref.93) the FH2 domain stepping towards the barbed end (2). The second FH2 repeats this process (3). The formin closed conformation prevents capping by other factors (4). Image in part a is modified, with permission, from Ref. 89 © (2004) Elsevier. Image in part b is modified, with permission, from Nature Ref. 92 © (2005) Macmillan publishers Ltd. All rights reserved.
