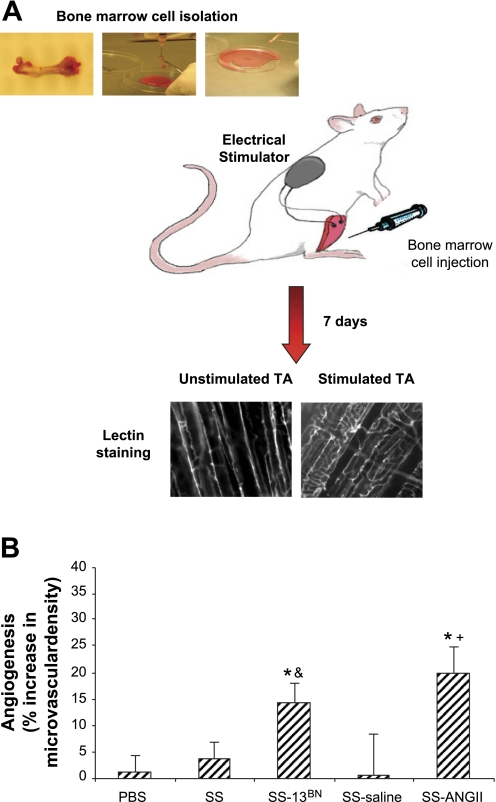
Fig. 1.
Effect of bone marrow cell (BMC) injection on the skeletal muscle angiogenesis induced by electrical stimulation. A: schematic illustration of the bone marrow injection protocol and vessel density analysis. B: percent increase in vessel density from unstimulated to stimulated tibialis anterior (TA) muscle of SS/Mcwi rats that received intramuscular PBS injection (n = 14) or BMC from SS/Mcwi (n = 11), BMC from SS-13BN (n = 11), BMC from SS/Mcwi infused with saline (n = 5) or BMC from SS/Mcwi infused with ANG II (n = 9). SS/Mcwi BMC failed to restore angiogenesis induced by electrical stimulation in SS/Mcwi rats. In contrast there was a significant increase in skeletal muscle vessel density of SS/Mcwi rats that received BMC from SS-13BN and SS/Mcwi rats infused with ANG II. Values are expressed as means ± SE. Unstimulated and stimulated vessel densities within each treatment were compared by paired t-test, *P < 0.05. Percent increase in vessel density was compared across groups by 1-way ANOVA, &P < 0.05 vs. SS; +P < 0.05 vs. SS-saline.