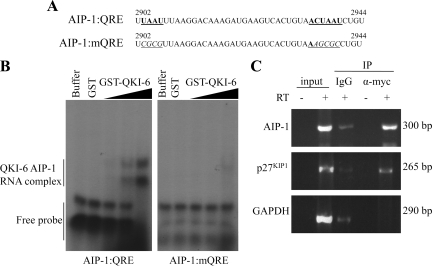
Figure 4.
The AIP-1 3′-UTR harbors a QKI response element (QRE). (A) The sequence of the human AIP-1 3′-UTR from nucleotides 2902–2944 is shown. The underlined and bold sequences denote the half-site and core QKI binding sites from left to right. The mutant AIP-1 sequences with mutations at the QRE sites are shown underlined and italicized. (B) Radioactive labeled RNA probes of the sequences shown in A were incubated with protein-RNA binding buffer alone (buffer), with GST, or with increasing amounts of GST-QKI-6. The samples were incubated at room temperature for 1 h and then separated by 8% Tris borate-EDTA-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel. The migration of the QKI-6/RNA complex and free RNA probe is indicated. (C) CRL2020 cells transduced with AdQKI-6 were lysed and protein–RNA interactions examined by coimmunoprecipitation. Cell extracts were lysed and incubated with IgG as a control and anti-myc antibodies to immunoprecipitate myc-epitope–tagged QKI-6. The QKI-6 bound RNA and input RNA were analyzed by semiquantitative RT-PCR, and the DNA fragments separated on a 2% agarose gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining.