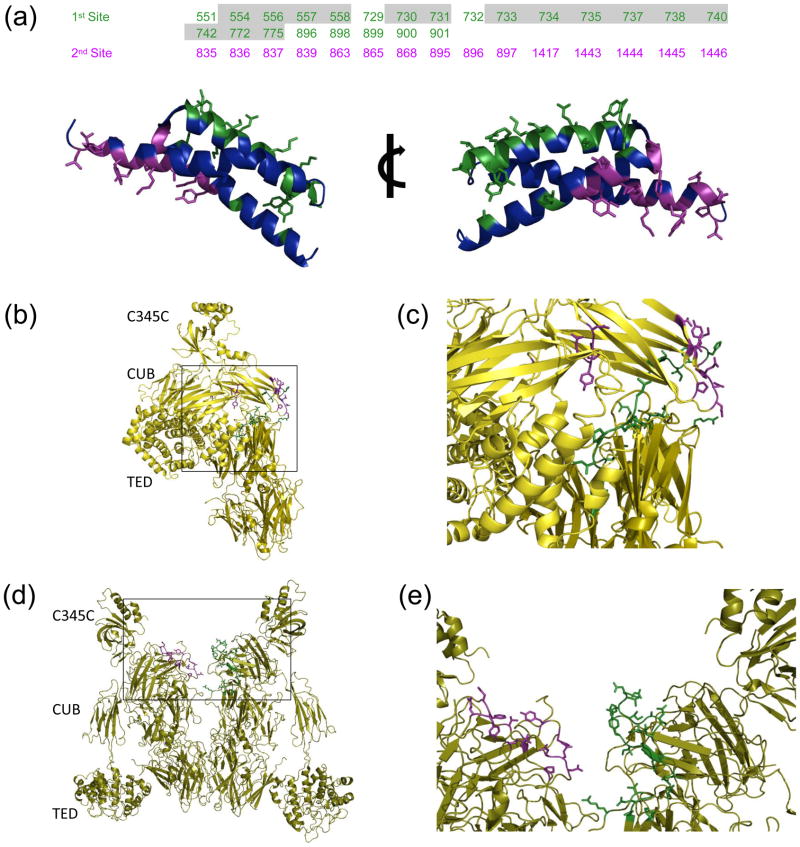
Figure 2. Molecular nature of SCIN binding sites to C3c and C3b.
The EBI PISA server was used identify and analyze intermolecular contacts within the C3b-SCIN and C3c-SCIN structures. (a) In the top panel, residues from the complement components are classified as belonging to either the first (green) or the second (purple) SCIN binding site described in the text; the residues shown here are greater than 5% buried in the structure of C3b-SCIN relative to unbound C3b. Numbering is based upon the sequence of human pre-pro-C3, and those which are buried in the structure of native C3 are shaded grey. Two rotated views of the SCIN protein are provided in the bottom panel. The sidechains from residues comprising the first site (green) and the second site (purple) are represented in ball-and-stick convention. (b) Location of residues comprising the first (green) and second (purple) SCIN binding sites in native C3. (c) Magnified view of the boxed region from panel b. (d) Location of residues comprising the first (green) and second (purple) SCIN binding sites within a C3b dimer generated by crystal symmetry. (e) Magnified view of the boxed region from panel d.