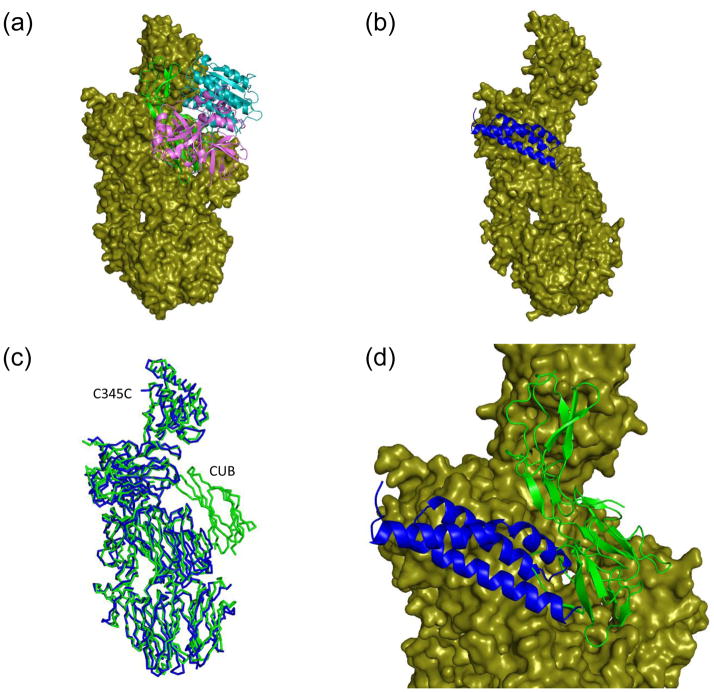
Figure 4. SCIN partially occludes the C3b binding site for factor B (fB).
Refined coordinates for the CVF-fB (RCSB code 3HRZ) 30 and the C3c-SCIN structure (drawn from RCSB code 3NMS) were superimposed by least-squares methods. (a) Representation of the CVF-fB structure, with CVF drawn as a molecular surface and fB drawn as ribbon. Domains which comprise the Ba (green) and Bb segments (cyan and purple) are colored separately. (b) Representation of the C3c-SCIN structure, with C3c drawn as a molecular surface and SCIN drawn as a blue ribbon. (c) Superposition of the Cα positions from the C3c-like component of panel a (green) and panel b (blue) demonstrates a high degree of structural identity. Note that C3c lacks the CUB domain found in CVF. (d) Magnified view of a merged superposition from panels a and b illustrates the steric clash between SCIN and the Ba region of fB. The Bb domains have been removed from this panel for clarity. The molecular surface shown here is drawn from the CVF-fB structure.