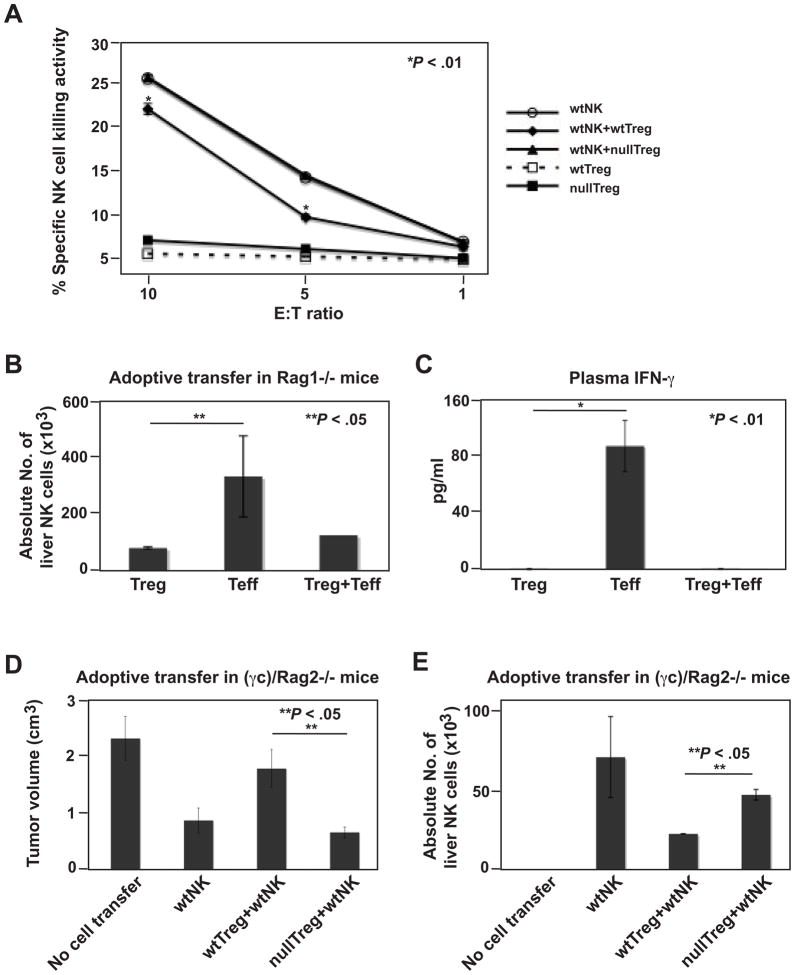
Figure 6.
Treg regulate NK cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity in a CD39-dependent manner. (A) Cd39 null Treg fail to suppress NK cell cytotoxicity in vitro. NK cells were cocultured at 1.5:1 and other ratios (not shown) with activated wt or Cd39 null Treg. The sorted CD4+GFP+ Treg were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 bound MACSiBead Particles and IL2 (100 ng/ml) for 72 h before coculture. (*P < .01, wtNK vs wtNK+wtTreg). (B) Absolute liver NK cell numbers in tumor-bearing Rag1−/− mice adoptively transferred with sorted wt lymphocytes (Treg, 0.1 × 106; Teff, 0.9 × 106) as indicated, followed by portal vein infusion of 2 × 105 luc-B16/F10 cells, on day 14. (C) Levels of IFN-γ in plasma obtained from mice in (B). (D) Tumor volumes of tumor-bearing (γc)/Rag2−/− mice adoptively transferred with lymphocytes (Treg, 1.0 × 106; NK, 1.0 × 106), followed by portal vein infusion of 2 × 105 luc-B16/F10 cells, on day 14. Mice received PBS as controls. (E) Absolute liver NK cell numbers in tumor-bearing mice of (D). Data are given as means ± SEM. *P < .01, **P < .05.