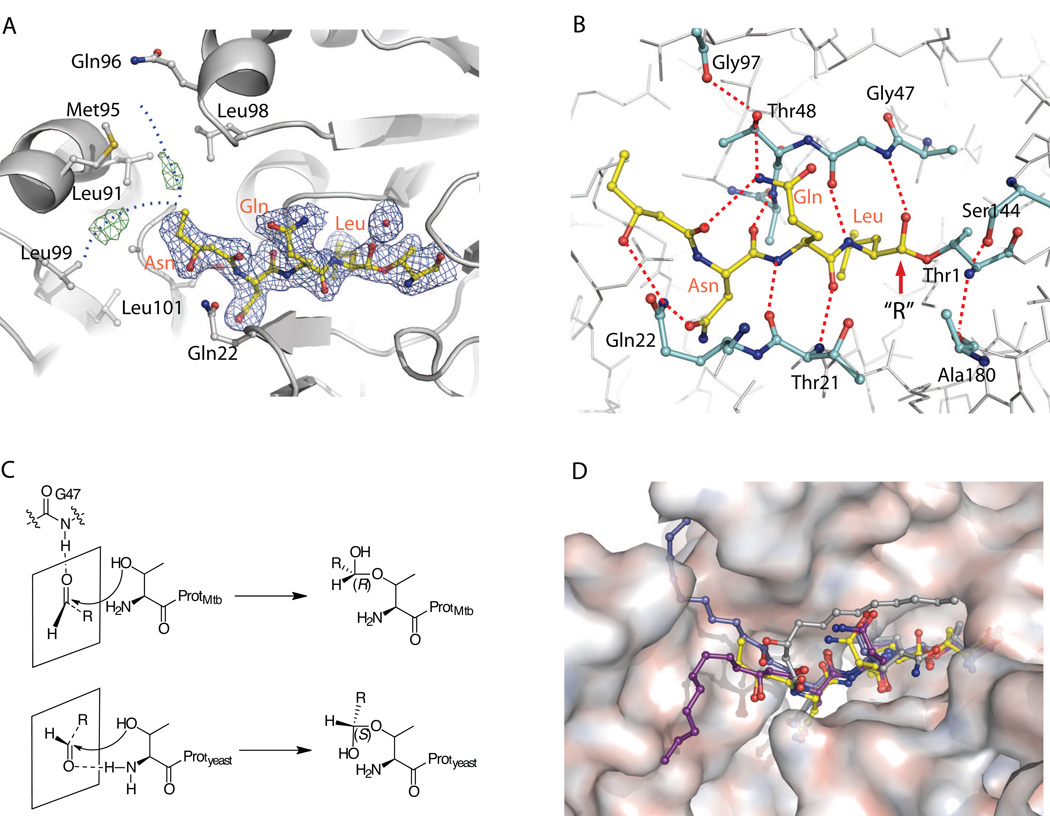
Figure 3.
Crystal structure of fellutamide B (1) bound to the Mtb proteasome
A) The 2Fo-Fc electron density map of fellutamide B shown at 1σ level is shown in blue mesh and the Fo-Fc map at 3σ in green mesh. The likely positions of the disordered alkyl tail from C24 to C32 of 1 are sketched by two dashed blue curves. B) The hydrogen-bonding network that stabilizes 1 in the substrate-binding pocket. The identities of selected proteasome residues are labeled in black, and the inhibitor residues are shown in orange. C) Scheme of the different stereochemistry of fellutamide B in the Mtb and yeast proteasomes. Upper panel, the carbonyl group takes trans-configuration, is hydrogen bonded with Gly-47 when approaching the Thr-1, and subsequently yields a (R)-hemiacetal; lower panel, the carbonyl group takes cis-configuration, is hydrogen bonded with NH2-Thr-1, and subsequently yields a (S)-hemiacetal. D) A surface view of the substrate-binding pocket of Mtb proteasome with the resolved structure of the fellutamide B (1) (yellow). The three structures of 1 bound to yeast proteasome β1, β2, and β5 are superimposed and shown in gray, blue, and purple, respectively (PDB ID 3D29).