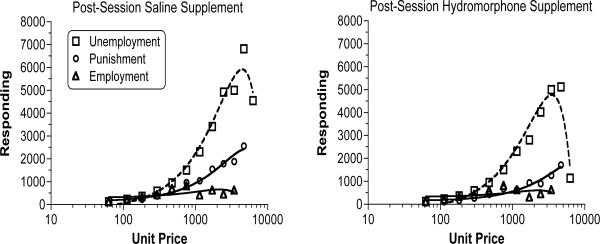
Figure 3.
Response output function produced by plotting group mean breakpoints for each economic contingency condition with the SAL supplement (left panel) and HYD supplement (right panel). Each panel shows polynomial regressions that were fitted to these data (for illustration only). The peaks of these bitonic functions estimate the Omax value, but the highest observed values were used as the calculated Omax points; these values are listed in Table 2. Each panel demonstrates that simulated Punishment (Drug Only + Money Loss) and Employment (Drug or Money) yielded progressively greater decreases in drug-seeking behavior, relative to Unemployment (Drug Only), with greater differences manifesting at higher UPs. Comparison across the two panels suggests that the HYD relative to the SAL supplement suppressed opioid seeking (i.e., decreased Omax) during the choice task for the Unemployment and Punishment analog conditions.