Figure 1. Stoichiometry of STAT1 nuclear import complex.
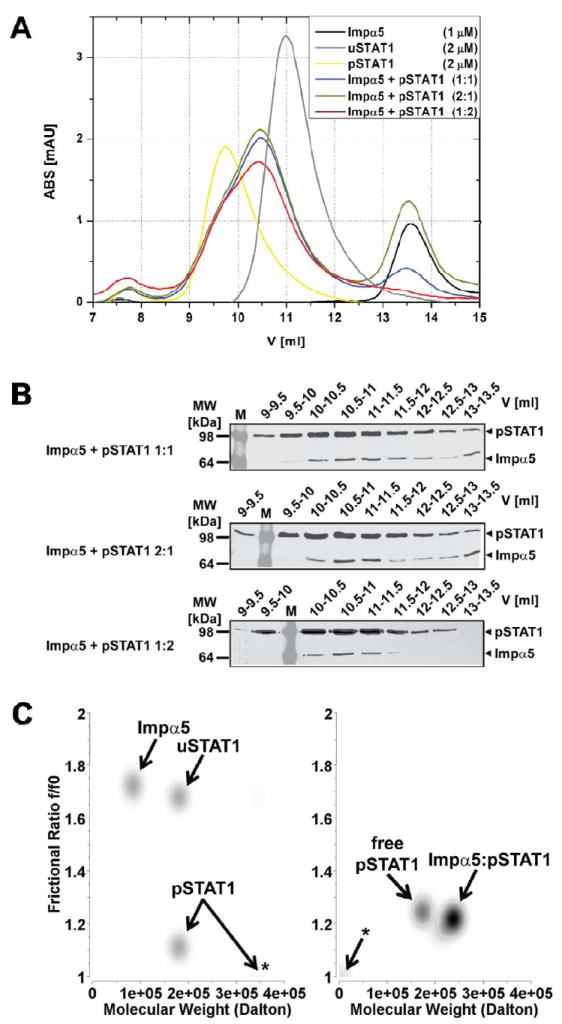
(A) Gel-filtration analysis of purified Strep-tagged unphosphorylated STAT1 (uSTAT1) and phosphorylated-Tyr701-STAT1 (pSTAT1), importin α5 (Impα5) and varying molar mixtures of pSTAT1 and Impα5. Free pSTAT1 elutes at 9.7 ml (presumably in a dimer-tetramer equilibrium) and free uSTAT1 at 11 ml (presumably as a dimer); the pSTAT1:importin α5 complexes formed at different molar ratios of pSTAT1 and Impα5 elute at identical elution volumes of 10.5 ml. Free Impα5, and excess Impα5 not bound in the pSTAT1:importin α5 complex elutes at 13.5 ml. (B) The indicated elution fractions obtained from the gel-filtration analyses of pSTAT1:importin α5 complexes shown in (A) were analyzed by Western Blot with anti-Strep antibody after 10% SDS-PAGE. (C) Sedimentation velocity analyses of uSTAT1, pSTAT1, importin α5, and complexes thereof. Graphical representation of molecular species detected by genetic algorithm–Monte Carlo analysis with molecular weights (M.W.) and frictional ratio in pseudo-3D plots. Left panel, Impα5, uSTAT1, and pSTAT1 were analyzed separately. Note an additional high molecular weight peak for pSTAT1 consistent with tetramerization (asterisk). Right panel, Impα:pSTAT1 was mixed and gel-filtrated. The peak fraction containing Impα:pSTAT1 complex was used in the ultracentrifugation experiment. Two molecular species with molecular weights of ~180 kDa and ~245 kDa were present. The latter was assigned to represent pSTAT1:importin α5 complex, whereas the former represents free pSTAT1 dimers. Asterisk, co-sedimenting salt in the reference cell.
