Fig. 2.
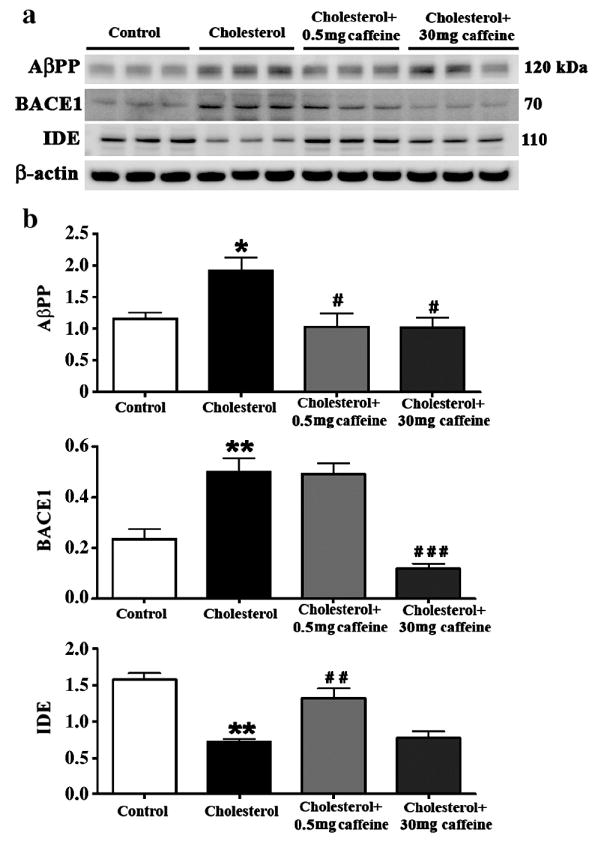
Caffeine dose-dependently regulates Aβ production and degradation in hippocampus from cholesterol-fed rabbits. Representative Western blots (a) and densitometric analysis (b) showing that while both 0.5 and 30 mg/day caffeine reduce the cholesterol-enriched diet-induced increase in AβPP, caffeine reduces BACE1 at 30 mg/day and increases IDE levels at 0.5 mg/day. Values are expressed as mean value ± SEM from three different experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 compared to controls, #p<0.05, # #p<0.01, # # #p<0.001 compared to rabbits fed with 2% cholesterol diet.
