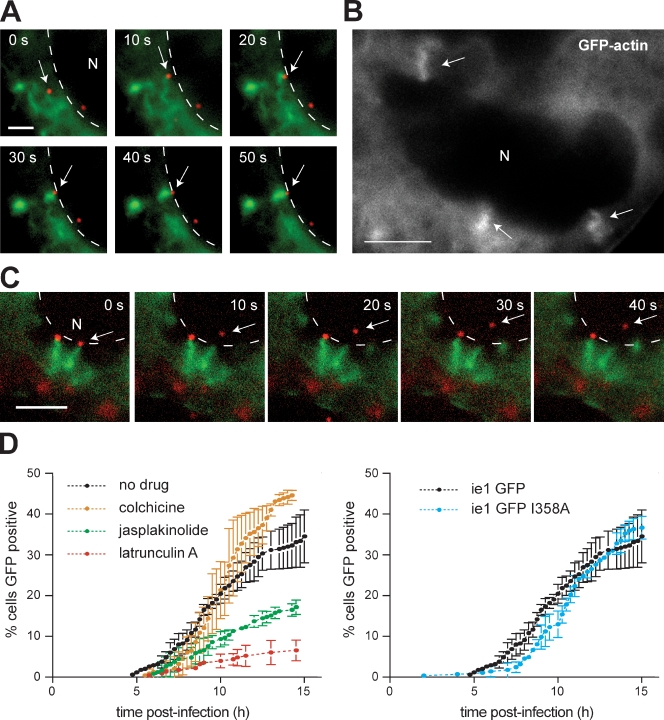
Figure 2.
Actin-based motility facilitates viral nuclear entry. (A) Time series of actin (green; EGFP-actin) and a nucleocapsid (red; 3mC virus; arrows) encountering the nuclear envelope (N; dashed lines). Bar, 2 µm. (B) Actin (EGFP-actin) corkscrew structures (arrows) associated with the periphery of the nucleus (N) are shown. Bar, 5 µm. (C) Time series of a nucleocapsid (red; 3mC; arrows) separating from its actin corkscrew (green; EGFP-actin) and entering the nucleus (N; nuclear periphery marked by dashed lines). Bar, 5 µm. (D) Graph of the percentage of High Five cells infected with AcMNPV ie-1 GFP that express visible EGFP at different times after infection. (left) ie-1 GFP in the absence or presence of cytoskeleton-disrupting drugs. (right) ie-1 GFP compared with ie-1 GFP I358A. Error bars indicate mean ± SD (n = 3 replicates).