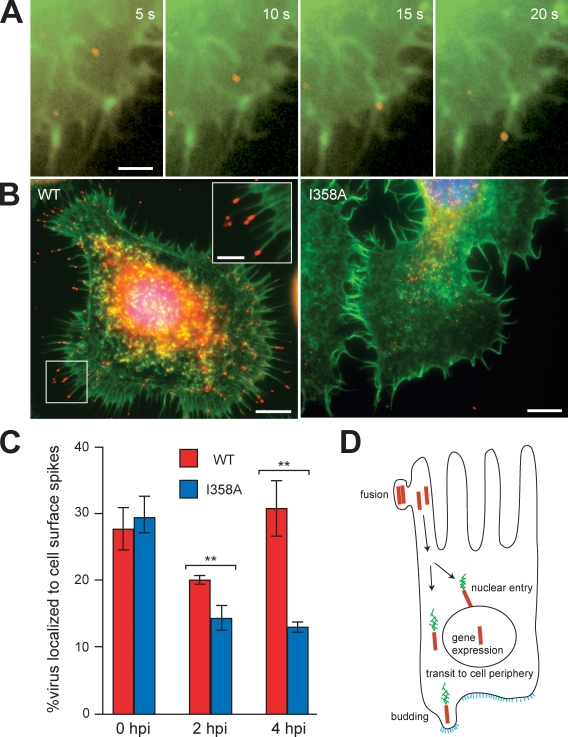
Figure 4.
AcMNPV actin-based motility drives virus localization to cell surface spikes. (A) Time series in 5-s intervals showing actin (green; EGFP-actin) and a 3mC virus (red) entering a cell surface spike. Bar, 2 µm. (B) Virus (red; anti-capsid immunofluorescence), actin (green; FITC-phalloidin), and DNA (blue; DAPI) in High Five cells infected with AcMNPV (left) or I358A AcMNPV (right) at 2 hpi, showing virus accumulation in cell surface spikes. Bars, 5 µm. Inset shows a magnified view of the boxed region. Bar, 2 µm. (C) Quantification of the percentage of 3mC (red) or 3mC I358A (blue) nucleocapsids localized to cell surface spikes at 0, 2, and 4 hpi in High Five cells. Error bars indicate mean ± SD. **, P < 0.01 (by unpaired t test). (D) Model of the roles of actin-based motility in baculovirus transport during the early phase of infection of a midgut epithelial cell. Colors represent nucleocapsids (red), actin (green), and viral glycoprotein GP64 (blue).