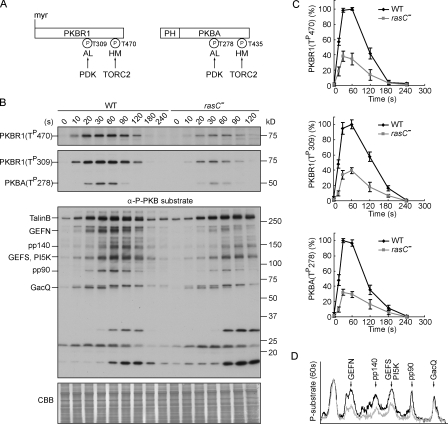
Figure 1.
RasC is required for the activation of the PKB pathway. (A) Schematic representation of the activation of PKBR1 and PKBA. PKBR1 is tethered to the plasma membrane via myristoylation, whereas PKBA is recruited to the plasma membrane by PIP3 via the PH domain. Upon chemoattractant stimulation, the two PKBs are activated through phosphorylation of their HMs by TORC2 and ALs by PDK. (B) Wild-type (WT) or rasC− cells were stimulated with cAMP, sampled at the indicated time points, and probed with anti–phospho-HM (first panel), anti–phospho-AL (second panel), or anti–phospho-substrate antibodies (third panel). The protein-transferred membrane was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) and shown as loading control (forth panel). Seven proteins, including TalinB, GEFN, GEFS, PI5K, and GacQ, are confirmed PKB substrates. Note that TalinB co-migrates with a non-PKB substrate band, and unmarked bands at the bottom part of the third panel are not PKB substrates (Kamimura et al., 2008). (C) Quantitative densitometry of the first and second panels of B, showing the mean intensity ± SD of the respective bands from three independent experiments. (D) Densitometric scan of the 60-s lanes of the third panel of B (wild type, black line; rasC−, gray line).