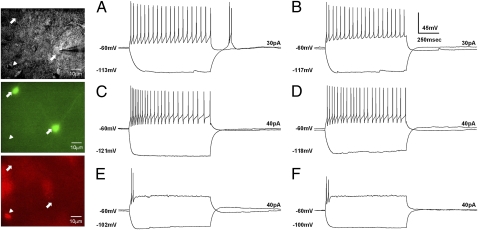
Fig. 2.
Electrophysiologically distinct classes of GABAergic neurons and PAG-RVM projection neurons in the vlPAG. The panel displays differential interference contrast (DIC) images (Top), GFP images (Middle), and retrograde-dye images (Bottom) of the patched neurons. Arrows indicate examples of GABAergic neurons, and the arrowhead indicates a PAG-RVM projection neuron. Two response patterns by either negative or positive step-current input are superposed in the traces. (A and B). GABAergic neurons. (A) Wild-type LTS-positive FS cells. (B) α1G−/− LTS-negative FS cell. (C–F) PAG-RVM projection neurons. (C) Wild-type FS cells. (D) α1G−/− FS cells. (E) Wild-type TS cells. (F) α1G−/− TS cells. The changes in the membrane potential and the applied currents are indicated in each trace.