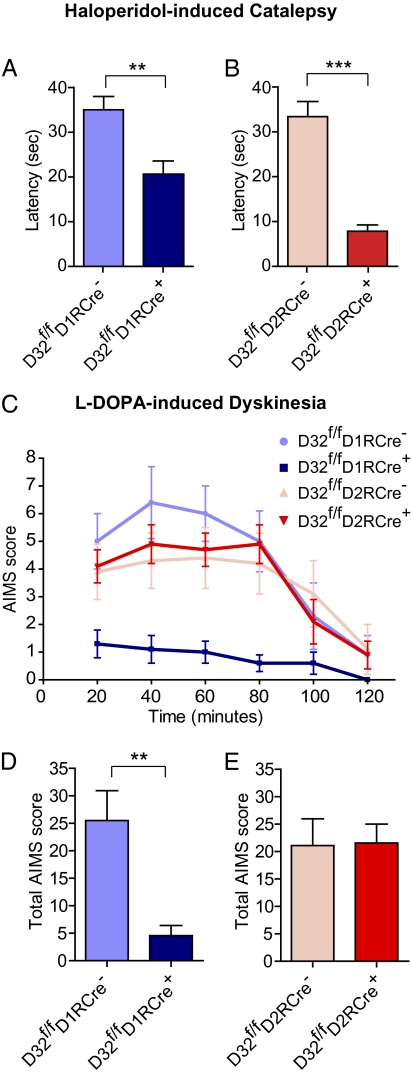
Fig. 6.
Differential contribution of striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons to haloperidol-induced catalepsy and L-DOPA–induced dyskinesia. (A and B) Mice were injected with 1.5 mg/kg haloperidol, and 60 min later catalepsy was assessed by measuring the latency until first movement in seconds. Bar graphs show group means ± SEM for mice from the indicated genotypes. n = 15–23 mice per genotype. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, unpaired two-tailed t test. (C and E) Mice received unilateral striatal injections of 6-OHDA and were treated for 10 d with L-DOPA. (C) Time profile of combined axial, limb, orolingual, and locomotive AIMs for mice from the indicated genotypes scored every 20 min over a 120-min period after the last drug administration. (D and E) Bar graphs showing group means ± SEM of total AIMs scored during the observation period for mice of the indicated genotypes. n = 7–9 mice per genotype. **P < 0.01, unpaired two-tailed Student t test.