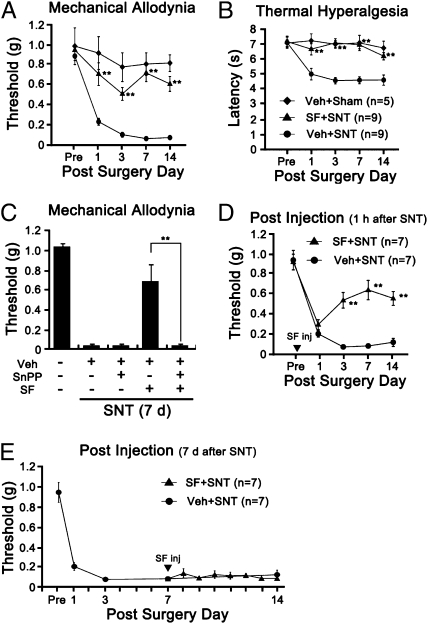
Fig. 5.
Sulforaphane reduces SNT-induced neuropathic pain behavior via HO-1 expression. (A and B) Mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia were measured using the SNT-injured mice with vehicle injection (Veh+SNT, n = 9), SNT-injured mice with sulforaphane injection (SF+SNT, n = 9, 10 mg/kg, in 3% DMSO, i.t.), and sham-operated mice with vehicle injection as the negative control (Veh+Sham, n = 5). (C) SnPP blocks the analgesic effects of sulforaphane. Sulforaphane (50 mg/kg) was i.p. injected into SNT-injured mice with or without SnPP (50 μmol/kg in 5% DMSO with PBS) at 1 h postsurgery. After 2 d, SnPP was injected (i.p.) again; and mechanical allodynia was measured on day 7 after surgery. (D and E) Sulforaphane inhibit the induction, but not the maintenance, of neuropathic pain. Mechanical allodynia was measured up to 14 d using SNT-injured mice with (SF+SNT) or without (Veh+SNT) sulforaphane injection (50 mg/kg, i.p.). Sulforaphane was given either 1 h (D) or 7 d (E) after SNT. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).