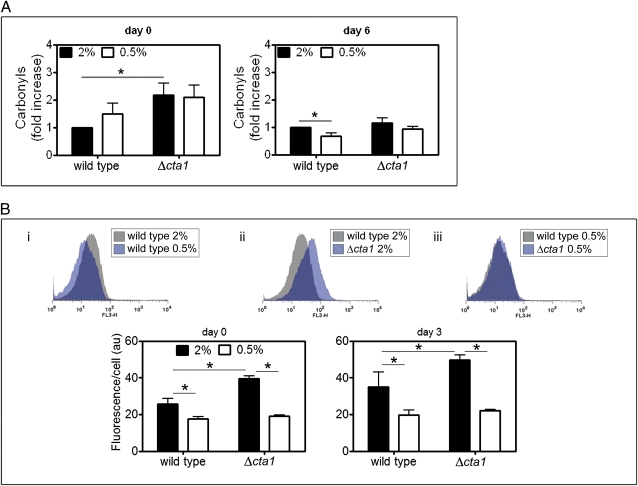
Fig. 4.
Effects of increased H2O2 induced by CR or by inactivation of CTA1 on oxidative damage to macromolecules. (A) Oxidative damage was assessed by measuring levels of oxidized proteins (carbonyls) in stationary phase wild-type and Δcta1 cells under non-CR and CR conditions. Levels of carbonyls were normalized at each time point to wild-type cell values under non-CR conditions (2% glucose). (B) Oxidative damage to proteins and lipids measured as autofluorescence of stationary phase wild-type and Δcta1 cells under non-CR and CR conditions. Histograms are representative of data collected at day 3. Values indicate mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical significance (*P < 0.05) was determined by Student's t-test.